确保人工智能的公平性:生成无偏差综合数据的策略
2023年11月16日 由 alex 发表
851
0
介绍
合成数据生成涉及创造与现实世界数据紧密相似的人造数据,但不含任何实际的个人信息,因此保护了隐私和保密性。然而,至关重要的是这些数据的生成方式必须是公平无偏的,以防止在人工智能应用中延续或放大现有的偏见。

公平合成数据的重要性
- 防止偏见:偏见数据在用于人工智能(AI)模型时可能导致不公平的结果,如在招聘、贷款或执法中的歧视。
- 道德人工智能发展:公平合成数据对于人工智能技术的伦理发展至关重要,确保其平等地服务于社会的所有部分。
- 合规性:很多地区有规定要求在自动化决策过程中确保公平和无歧视。
生成公平合成数据的方法论
- 理解和识别偏见:识别可能渗透数据集的各种偏见类型(如选择偏见、测量偏差和算法偏差)。
- 多样化数据来源:合并广泛的来源以涵盖不同的人口统计、地理和社会经济背景。
- 算法干预:使用特别设计来生成无偏数据的算法,包括类似重新采样、重新加权和合成少数群体过采样等技术。
生成公平合成数据的挑战
- 偏见复杂性:偏见可能根深蒂固且多方面,使得识别和减轻变得困难。
- 数据隐私问题:平衡对现实数据的需求与保护个人隐私的需要。
- 公平的动态性:公平的定义可能在不同文化和时间中变化,要求对合成数据生成过程进行持续的监控和调整。
潜在的解决方案和最佳实践
- 定期审计:对合成数据集和生成它们的算法进行定期审计,以确保持续的公平性。
- 透明度和责任:保持数据生成和使用的透明度,并确保对不公平结果的责任。
- 与多样化团队合作:在开发过程中涉及多样化的团队,带来不同的视角并减少无意识偏见的风险。
- 道德准则和框架:制定并遵守专门为合成数据生成而设计的伦理准则和框架。
代码
在Python中生成公平合成数据包括多个步骤,从理解和预处理数据到应用确保公平性的技术。我们将通过一个完整的示例,包括代码和图表,来说明这一过程。请注意,具体的方法和技术可能会根据数据和你工作的上下文而有所不同。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sdv.metadata import MultiTableMetadata
# Load your dataset (this is a placeholder path)
real_data = pd.read_csv('Scripted_1.csv')
real_data.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=False)
real_data.rename(columns={'index': 'row_number'}, inplace=True)
metadata = MultiTableMetadata()
metadata.detect_from_dataframes({
'table_name': real_data
})
print('Auto detected data:\n')
metadata.visualize()
# Generate synthetic data
synthesizer = CTGANSynthesizer(metadata.tables.get('table_name'))
synthesizer.fit(real_data)
synthetic_data = synthesizer.sample(num_rows=500)
synthetic_data.head()
如果合成数据显示出偏差,你可能需要调整你的模型。这可能包括:
- 改变模型的参数。
- 使用像重新加权数据这样的公平增强技术。
- 应用为公平数据生成专门设计的算法。
metadata.tables.get('table_name')get('table_name'){
"primary_key": "row_number",
"METADATA_SPEC_VERSION": "SINGLE_TABLE_V1",
"columns": {
"row_number": {
"sdtype": "id"
},
"angry": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"disgust": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"fear": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"happy": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"sad": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"surprise": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"neutral": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"dominant_emotion": {
"sdtype": "categorical"
},
"face_x": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"face_y": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"face_w": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
},
"face_h": {
"sdtype": "numerical"
}
}
}# Example: Comparing the distribution of a sensitive attribute
def plot_distributions(real_data, synthetic_data, column):plot_distributions(real_data, synthetic_data, column):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.hist(real_data[column], bins=20, alpha=0.7, label='Real Data')
plt.title('Real Data Distribution')
plt.xlabel(column)
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist(synthetic_data[column], bins=20, alpha=0.7, label='Synthetic Data')
plt.title('Synthetic Data Distribution')
plt.xlabel(column)
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.show()
# Plot distributions for a sensitive attribute
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'angry')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'disgust')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'fear')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'happy')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'sad')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'surprise')
plot_distributions(X_train, synthetic_data, 'neutral')
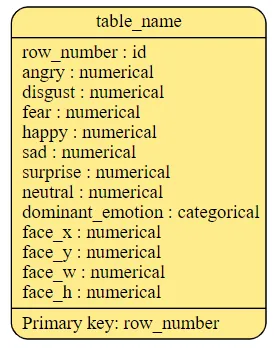
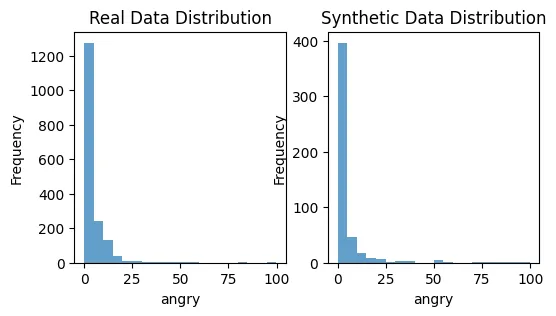
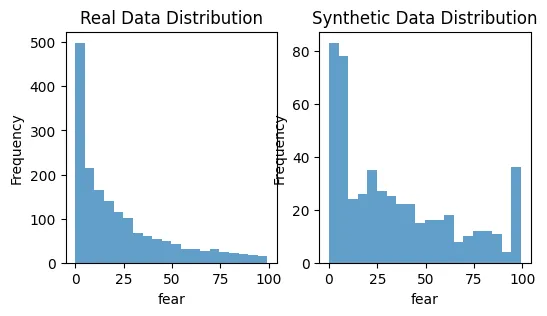
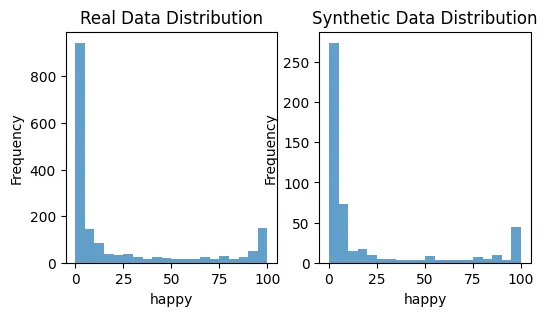
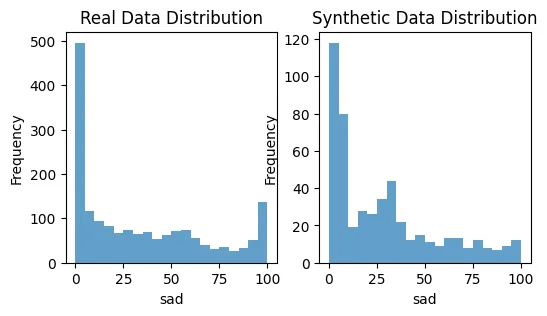
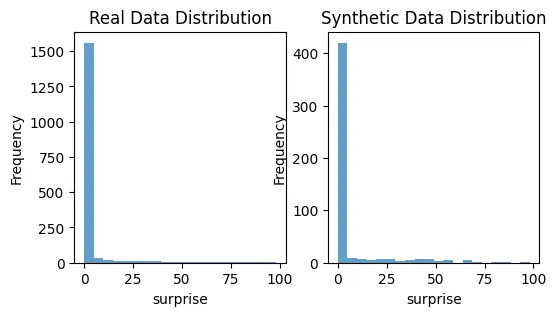
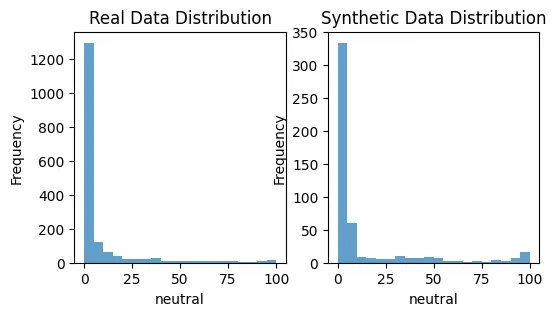
这是一个基础示例帮助你开始。公平的合成数据生成领域是复杂的,往往需要特定领域的知识和迭代测试才能做好。关键是要不断监控和调整你的方法,确保合成数据尽可能无偏见。
结论
生成公平的合成数据对于负责任地开发和部署人工智能系统至关重要。这需要在使用先进技术模拟真实数据和确保这些数据不延续现有偏见之间谨慎平衡。通过采用全面的方法论,直面挑战,并坚持最佳实践和伦理标准,我们能够创造出既有用又公平的合成数据。
文章来源:https://medium.com/@evertongomede/ensuring-fairness-in-ai-strategies-for-generating-bias-free-synthetic-data-8875fe18bebd

欢迎关注ATYUN官方公众号
商务合作及内容投稿请联系邮箱:bd@atyun.com
上一篇
回顾LLM的发展历程
热门企业
热门职位
写评论取消
回复取消






























