使用ImageBind和Qdrant在电子商务网站上执行图像驱动的反向图像搜索
简介
1950 年,当阿兰-图灵在他的论文《计算机械与智能》中提出 "机器智能 "一词时,谁也没有想到,在未来的某一天,它会导致在不同领域利用人工智能进行各种创新。在用户中非常流行和重要的一个领域是网上购物。随着电子商务的迅猛发展,用户越来越依赖视觉线索来引导他们做出购买决策。为了应对消费者行为的这一转变,图像驱动的产品搜索已成为提升购物体验的有力工具。亚马逊、Myntra、Ajio 和 Meesho 等电子商务平台正在广泛使用图像驱动的产品搜索。
你一定对购物网站上的图片驱动搜索不陌生。这种创新方法利用图片中的视觉内容,让用户更直观、更高效地搜索产品。购物者只需上传或捕捉一张图片,就能在庞大的目录中快速找到相似或相关的商品。无论是寻找时尚灵感、家居装饰创意,还是特定产品推荐,图片驱动搜索都能为用户提供动态的个性化购物体验,满足个人喜好和品味。
通过使用 Meta 公司最近开发的一体化嵌入模型,我们可以使结果更加精确: ImageBind。但在使用嵌入模型之前,我们需要使用矢量数据库来存储它们。
说到图像搜索,矢量数据库尤其具有变革性。传统的图像搜索方法通常依赖于元数据标签或文本描述,这在捕捉图像丰富的视觉内容方面可能会受到限制。有了矢量数据库,图像被转换成高维矢量,通过更准确、更细致的相似性比较,囊括了图像的视觉特征。这意味着,用户可以根据视觉相似性搜索图像,从而实现从图像中精确搜索电子商务产品的任务。然而,在使用矢量数据库时,我们会面临一个难题:哪个数据库最适合我们的应用?
在这里,我选择了 Qdrant Vector数据库,它为高级人工智能应用提供了近似近邻搜索的高级搜索算法,即 HNSW 算法。Meesho 已经在使用 Qdrant Vector数据库,但结果仍然不是很准确。我们可以通过整合 Qdrant 和 ImageBind 嵌入模型来提高结果的准确性。
使用Qdrant反向搜索产品图片
让我们先安装依赖项,然后开始反向产品图片搜索。
%pip install opendatasets gradio qdrant-client transformers sentence_transformers sentencepiece tqdm
加载数据集
使用 opendatasets 库,使用用户名和密钥下载 Kaggle 数据集。你可以访问 Kaggle 的 "设置 "页面获取用户名和密钥。点击 "访问 API 密钥",就会下载一个 kaggle.json 文件。该文件将包含你的用户名和 API 密钥。
import opendatasets as od
od.download("https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/vikashrajluhaniwal/fashion-images")
现在,让我们把图像存储在一个列表中,这样我们就可以轻松访问图像了。
import random
import gradio as gr
from PIL import Image
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
from qdrant_client.http import models
import tempfile
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
import os
def get_image_paths(directory):
# Initialize an empty list to store the image paths
image_paths = []
# Iterate through all files and directories within the given directory
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
# Check if the file has an image extension (e.g., .jpg, .png, .jpeg, etc.)
if file.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.gif', '.bmp')):
# Construct the full path to the image file
image_path = os.path.join(root, file)
# Append the image path to the list
image_paths.append(image_path)
return image_paths
# Directory paths
women_directory = './fashion-images/data/Footwear_Women/Images/images_with_product_ids/'
men_directory = './fashion-images/data/Footwear_Men/Images/images_with_product_ids/'
girls_directory = './fashion-images/data/Apparel_Girls/Images/images_with_product_ids/'
boys_directory = './fashion-images/data/Apparel_Boys/Images/images_with_product_ids/'
# Get image paths for different categories
image_paths_Women = get_image_paths(women_directory)
image_paths_Men = get_image_paths(men_directory)
image_paths_Girls = get_image_paths(girls_directory)
image_paths_Boys = get_image_paths(boys_directory)
all_image_paths = []
all_image_paths.append(image_paths_Boys)
all_image_paths.append(image_paths_Girls)
all_image_paths.append(image_paths_Men)
all_image_paths.append(image_paths_Women)
初始化Qdrant矢量数据库
使用内存存储初始化 Qdrant 客户端。集合名称为 "imagebind_data",我们将使用余弦距离。
# Initialize Qdrant client and load collection
client = QdrantClient(":memory:")
client.recreate_collection(collection_name = "imagebind_data",
vectors_config = {"image": models.VectorParams( size = 1024, distance = models.Distance.COSINE ) } )
使用 ImageBind 进行图像嵌入
ImageBind 是由 Meta AI 的 FAIR 实验室开发的一种创新模型。该模型旨在学习六种不同模式的联合嵌入:图像、文本、音频、深度、热和 IMU 数据。ImageBind 的主要特点之一是,它能够在不需要所有配对数据组合的情况下学习这种联合嵌入。研究发现,只有图像配对数据才能有效地将各种模态绑定在一起。这种独特的能力使 ImageBind 能够利用最新的大规模视觉语言模型,并通过利用这些模型与图像的自然配对,将其零拍摄功能扩展到新的模态。
我们将使用 ImageBind 创建嵌入,但在深入学习之前,我们先来了解一下安装 ImageBind 所需的一些步骤。
克隆 Imagebind 的 git 仓库:
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/ImageBind.git
更改目录:
cd Imagebind
编辑 requirements.txt 文件: 如果出现错误或问题,请删除 Mayavi 和 Cartopy。
安装需求:
pip install -r requirements.txt
返回系统。
然后,加载模型。
import sys
sys.path.append("./ImageBind/")
device = "cuda"
import imagebind
from imagebind.models import imagebind_model
model = imagebind_model.imagebind_huge(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
model.to(device)
初始化模型后,我们将创建嵌入。
from imagebind.models.imagebind_model import ModalityType
from imagebind import data
import torch
embeddings_list = []
for image_paths in [image_paths_Boys, image_paths_Girls, image_paths_Men, image_paths_Women]:
inputs = {ModalityType.VISION: data.load_and_transform_vision_data(image_paths, device)}
with torch.no_grad():
embeddings = model(inputs)
embeddings_list.append(embeddings)
然后,我们将用生成的嵌入式数据更新 Qdrant Vector数据库。
import uuid
points = []
# Iterate over each embeddings and corresponding image paths
for idx, (embedding, image_paths) in enumerate(zip(embeddings, all_image_paths)):
for sub_idx, sample in enumerate(image_paths):
# Convert the sample to a dictionary
payload = {"path": sample}
# Generate a unique UUID for each point
point_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
points.append(models.PointStruct(id=point_id,
vector= {"image": embedding['vision'][sub_idx]},
payload=payload)
)
client.upsert(collection_name="imagebind_data", points=points)
我们将准备一个处理函数,将图像作为输入,并借助嵌入进行反向图像搜索。
def process_text(image_query):
user_query = [image_query]
dtype, modality = ModalityType.VISION, 'image'
user_input = {dtype: data.load_and_transform_vision_data(user_query, device)}
with torch.no_grad():
user_embeddings = model(user_input)
image_hits = client.search(
collection_name='imagebind_data',
query_vector=models.NamedVector(
name="image",
vector=user_embeddings[dtype][0].tolist()
)
)
# Check if 'path' is in the payload of the first hit
if image_hits and 'path' in image_hits[0].payload:
return (image_hits[0].payload['path'])
else:
return None
使用 Gradio 进行部署
既然我们已经准备好了处理镜像功能,那么我们就可以通过定义 Gradio 的接口来使用 Gradio 进行部署。
import tempfile
tempfile.tempdir = "./fashion-images/data"
# Gradio Interface
iface = gr.Interface(
title="Reverse Image Search with Imagebind",
description="Leveraging Imagebind to perform reverse image search for ecommerce products",
fn=process_text,
inputs=[
gr.Image(label="image_query", type="filepath")
],
outputs=[
gr.Image(label="Image")],
)
使用产品类别搜索图片
如果要使用产品类别搜索图片,就必须定义一些函数。我们将定义一个从类别中获取图片的函数。
# Define function to get images of selected category
def get_images_from_category(category):
# Convert category to string
category_str = str(category)
# Directory path for selected category
category_dir = f"./fashion-images/data/{category_str.replace(' ', '_')}/Images/images_with_product_ids/"
# List of image paths
image_paths = os.listdir(category_dir)
# Open and return images
images = [Image.open(os.path.join(category_dir, img_path)) for img_path in image_paths]
return images
然后列出产品类别。
# Define your product categories
product_categories = ["Apparel Boys", "Apparel Girls", "Footwear Men", "Footwear Women"]
之后,我们将定义一个用于选择类别的函数。
# Define function to handle category selection
def select_category(category):
# Get images corresponding to the selected category
images = get_images_from_category(category)
# Return a random image from the list
return random.choice(images)
使用 Gradio 进行部署
现在,我们将为类别选择创建 Gradio 界面组件,如类别下拉和提交按钮。
# Create interface components for the category selection
category_dropdown = gr.Dropdown(product_categories, label="Select a product category")
submit_button = gr.Button()
images_output = gr.Image(label="Images of Selected Category")
之后,我们将创建一个 Gradio 接口,并传递函数和组件。
category_search_interface = gr.Interface(
fn=select_category,
inputs=category_dropdown,
outputs=images_output,
title="Category-driven Product Search for Ecommerce",
description="Select a product category to view a random image from the corresponding directory.",
)
合并两个 Gradio 界面
我们部署了两个 Gradio 界面:一个是反向图片搜索,另一个是使用产品类别进行图片搜索。如果我们能在一个应用程序中同时看到这两个界面呢?这可以通过使用 TabbedInterface 来实现。
# Combine both interfaces into the same API
combined_interface = gr.TabbedInterface([iface, category_search_interface])
# Launch the combined interface
combined_interface.launch(share=True)
现在,我们将获得一个内部 URL 和一个公共 URL。应用程序就有两个选项卡了。
标签 0:利用 ImageBind 进行反向图像搜索,用于电子商务
表 1:用于电子商务的类别驱动型产品搜索
示例
让我们看看我们的应用程序是如何运行的。
我传入了一张穿着无袖连衣裙的女孩图片。让我们看看我们的应用程序能否从产品中找到类似的图片。
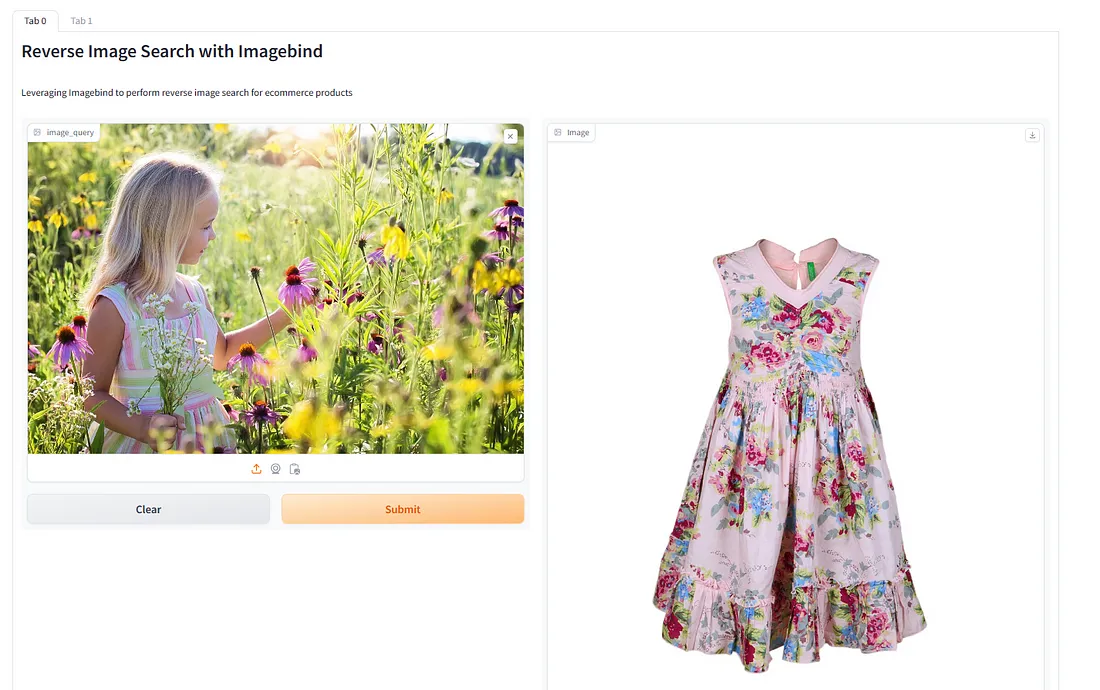
该应用程序找到了一件非常相似的衣服。
让我们试试将 "鞋 "作为图片传过去。我传入了一张三个人穿着运动鞋的脚的图片。让我们看看结果。
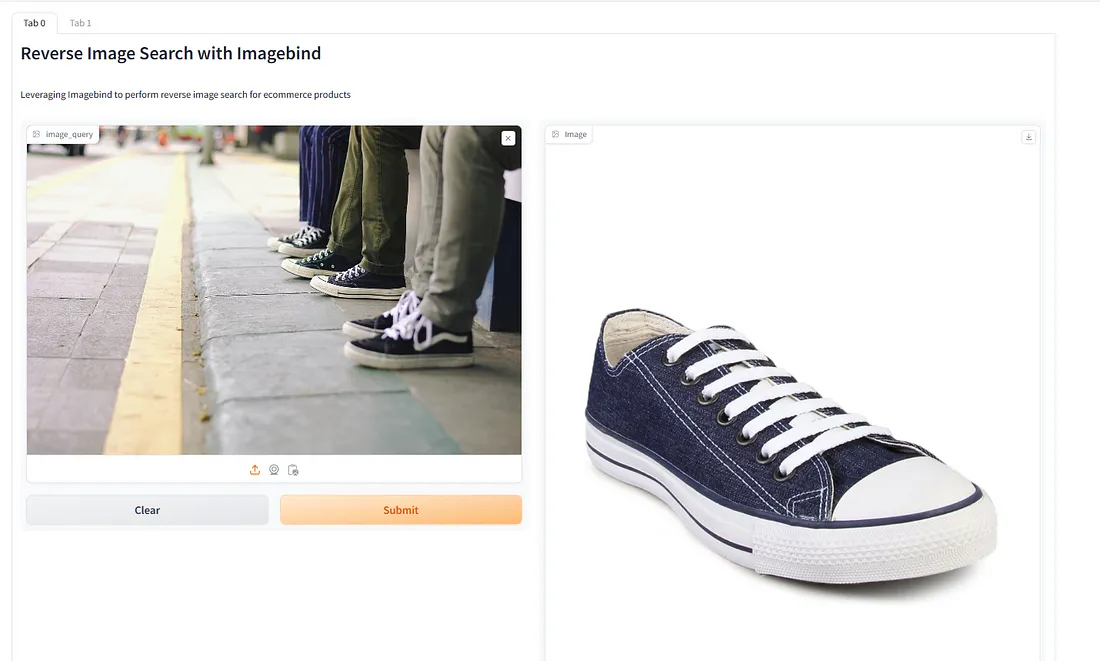
结果令人印象深刻。输出是相同风格的运动鞋。
让我们试试类别搜索。例如,我想查看 "男孩服装 "类别中有哪些产品。Gradio 只能输出一张图片,但在此应用中,每次搜索都不会输出相同的图片。
第一次搜索得到了一件白色 T 恤的图片。让我们再搜索一次,看看还有哪些其他的 T 恤。
结果是一件蓝灰色的 T 恤。因此,结果不会重复。很好!
结论
有了Qdrant Vector DB,电子商务产品的反向图片搜索就成为可能。我们从结果中看到了如何通过上传图片执行反向图片搜索,并从选定的产品类别中获取类似产品的图片。在ImageBind嵌入模型的帮助下,结果非常准确。































