在LlamaIndex中自定义属性图索引
背景介绍
属性图索引是 LlamaIndex 的一个出色补充,也是以前知识图谱集成的升级版。现在的数据表示略有不同。在以前的集成中,图是用三元组表示的,但现在我们有了一个适当的属性图集成,其中节点有标签和可选的节点属性。
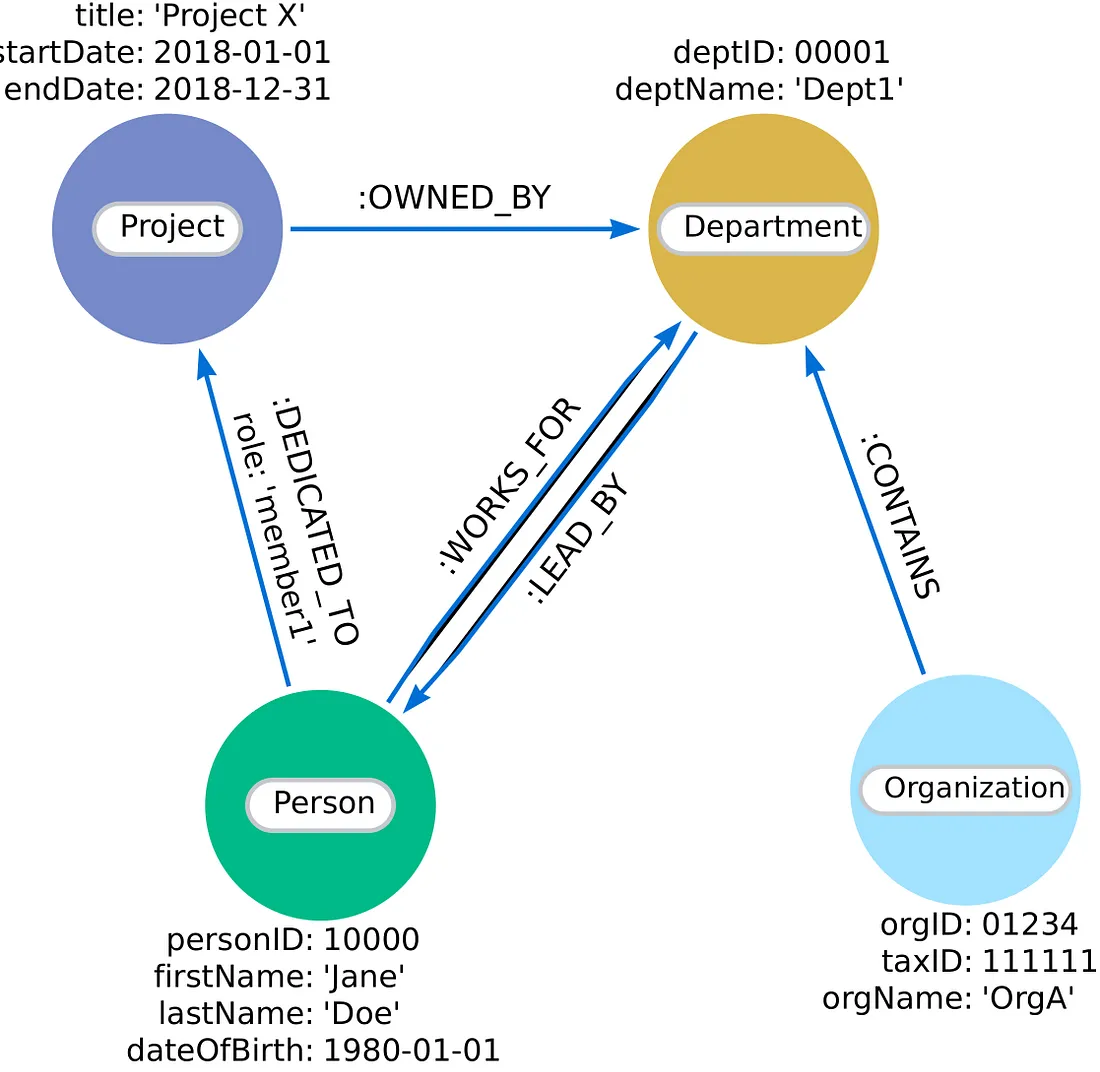
每个节点都有一个标签,标明其类型,如个人、组织、项目或部门。节点和关系还可以存储其他相关详细信息的节点属性,如出生日期或项目开始和结束日期,如本示例所示。
属性图索引的设计是模块化的,因此你可以使用一个或多个(自定义)知识图构造函数以及检索器,这使它成为你构建第一个知识图或根据你的需要自定义实现的绝佳工具。
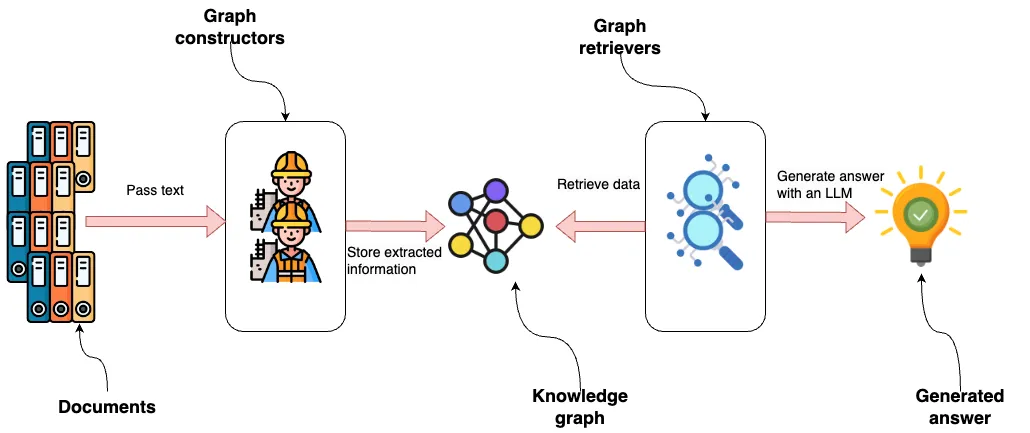
图片说明了 LlamaIndex 中的属性图集成,首先是将文档传递给图构造器。这些构造器是模块化组件,可提取结构化信息,然后将其存储在知识图谱中。知识图谱可以使用各种模块或自定义模块来构建,这凸显了系统适应不同数据源或提取需求的灵活性。
然后,图形检索器访问知识图谱以检索数据。这一阶段也是模块化的,允许使用多个检索器或定制解决方案来查询特定类型的数据或图中的关系。
LLM 使用检索到的数据生成答案,代表从流程中得出的输出或见解。该流程强调系统的高度适应性和可扩展性,每个组件都可以独立修改或替换,以增强整体功能或满足特定要求。
在本文中,你将学习如何:
- 使用模式引导提取构建知识图谱
- 结合使用文本嵌入和词语相似性技术进行实体重复删除
- 设计自定义图检索器
- 使用自定义检索器实施问题解答流程
代码可在 GitHub 上获取。
环境设置
我们将使用 Neo4j 作为底层图形存储。最简单的入门方法是使用 Neo4j Aura 的免费实例,它提供 Neo4j 数据库的云实例。或者,你也可以下载 Neo4j Desktop 应用程序并创建本地数据库实例,从而建立 Neo4j 数据库的本地实例。
from llama_index.graph_stores.neo4j import Neo4jPGStore
username="neo4j"
password="stump-inlet-student"
url="bolt://52.201.215.224:7687"
graph_store = Neo4jPGStore(
username=username,
password=password,
url=url,
)
此外,你还需要一个可用的 OpenAI API 密钥:
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-"
数据集
我们将使用 Diffbot 的新闻文章样本数据集,为了方便访问,我已将其放在 GitHub 上。

由于属性图索引是通过文档操作的,因此我们必须将新闻中的文本包装成 LlamaIndex 文档:
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.core import Document
news = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tomasonjo/blog-datasets/main/news_articles.csv")
documents = [Document(text=f"{row['title']}: {row['text']}") for i, row in news.iterrows()]
图形构造
LlamaIndex 提供多种开箱即用的图形构造器。在本例中,我们将使用 SchemaLLMPathExtractor,它允许我们定义要从文档中提取的图形结构的模式。
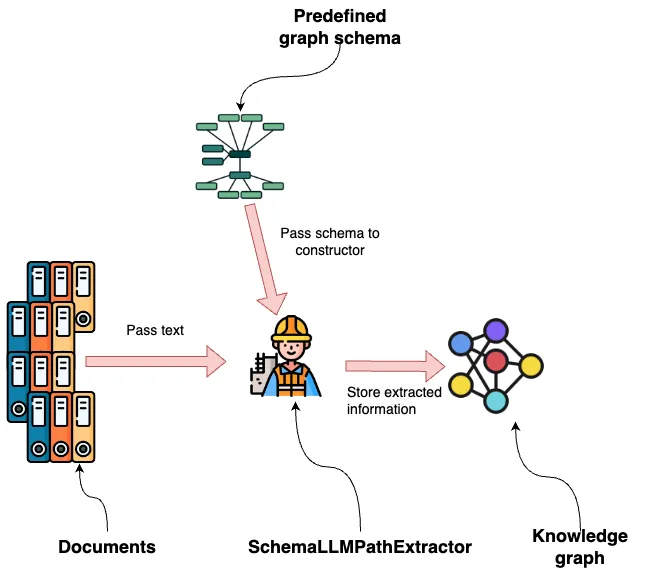
我们首先要定义希望 LLM 提取的节点和关系类型:
entities = Literal["PERSON", "LOCATION", "ORGANIZATION", "PRODUCT", "EVENT"]
relations = Literal[
"SUPPLIER_OF",
"COMPETITOR",
"PARTNERSHIP",
"ACQUISITION",
"WORKS_AT",
"SUBSIDIARY",
"BOARD_MEMBER",
"CEO",
"PROVIDES",
"HAS_EVENT",
"IN_LOCATION",
]
正如你所看到的,我们的图提取重点是人和组织。接下来,我们指定与每个节点标签相关的关系:
# define which entities can have which relations
validation_schema = {
"Person": ["WORKS_AT", "BOARD_MEMBER", "CEO", "HAS_EVENT"],
"Organization": [
"SUPPLIER_OF",
"COMPETITOR",
"PARTNERSHIP",
"ACQUISITION",
"WORKS_AT",
"SUBSIDIARY",
"BOARD_MEMBER",
"CEO",
"PROVIDES",
"HAS_EVENT",
"IN_LOCATION",
],
"Product": ["PROVIDES"],
"Event": ["HAS_EVENT", "IN_LOCATION"],
"Location": ["HAPPENED_AT", "IN_LOCATION"],
}
例如,一个人可以有以下关系:
- 工作地点
- 董事会成员
- 首席执行官
- HAS_EVENT
除了 EVENT 节点标签稍显模糊外,该模式非常具体,允许 LLM 捕捉各种类型的信息。
现在,我们已经定义了图模式,可以将其输入 SchemaLLMPathExtractor 并用于构建图:
from llama_index.core import PropertyGraphIndex
kg_extractor = SchemaLLMPathExtractor(
llm=llm,
possible_entities=entities,
possible_relations=relations,
kg_validation_schema=validation_schema,
# if false, allows for values outside of the schema
# useful for using the schema as a suggestion
strict=True,
)
NUMBER_OF_ARTICLES = 250
index = PropertyGraphIndex.from_documents(
documents[:NUMBER_OF_ARTICLES],
kg_extractors=[kg_extractor],
llm=llm,
embed_model=embed_model,
property_graph_store=graph_store,
show_progress=True,
)
本代码从 250 篇新闻文章中提取图表信息,但你可以根据需要调整数量。总共有 2,500 篇文章。
请注意,使用 GPT-4o 提取 250 篇文章大约需要 7 分钟。不过,你可以通过参数 num_workers 来并行加速这一过程。
我们可以可视化一个小的子图来查看存储的内容。
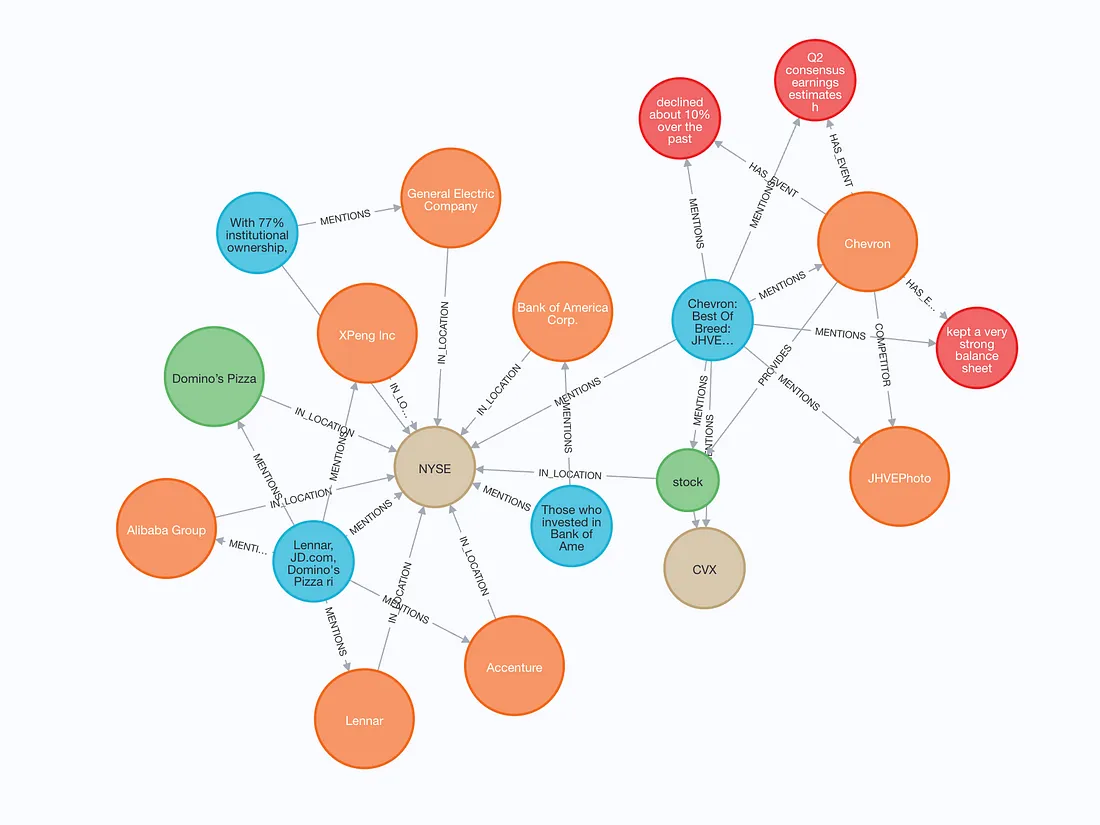
构建的图包含文本块(蓝色)以及文本和嵌入。如果文本块中提到了实体,则文本块与实体之间存在 MENTIONS 关系。此外,实体还可以与其他实体发生关系。
实体重复删除
实体重复删除或消歧是图构建中一个重要但经常被忽视的步骤。从本质上讲,这是一个清理步骤,即尝试匹配代表单一实体的多个节点,并将它们合并为一个节点,以提高图结构的完整性。
例如,在我们构建的图中,我发现了一些可以合并的例子。
我们将结合使用文本嵌入相似性和词距来查找潜在的重复内容。我们首先要定义图中实体的向量索引:
graph_store.structured_query("""
CREATE VECTOR INDEX entity IF NOT EXISTS
FOR (m:`__Entity__`)
ON m.embedding
OPTIONS {indexConfig: {
`vector.dimensions`: 1536,
`vector.similarity_function`: 'cosine'
}}
""")下一个 Cypher 查询会查找重复数据,而且非常复杂。我、迈克尔-亨格(Michael Hunger)和埃里克-蒙克(Eric Monk)花了几个小时才完善它:
similarity_threshold = 0.9
word_edit_distance = 5
data = graph_store.structured_query("""
MATCH (e:__Entity__)
CALL {
WITH e
CALL db.index.vector.queryNodes('entity', 10, e.embedding)
YIELD node, score
WITH node, score
WHERE score > toFLoat($cutoff)
AND (toLower(node.name) CONTAINS toLower(e.name) OR toLower(e.name) CONTAINS toLower(node.name)
OR apoc.text.distance(toLower(node.name), toLower(e.name)) < $distance)
AND labels(e) = labels(node)
WITH node, score
ORDER BY node.name
RETURN collect(node) AS nodes
}
WITH distinct nodes
WHERE size(nodes) > 1
WITH collect([n in nodes | n.name]) AS results
UNWIND range(0, size(results)-1, 1) as index
WITH results, index, results[index] as result
WITH apoc.coll.sort(reduce(acc = result, index2 IN range(0, size(results)-1, 1) |
CASE WHEN index <> index2 AND
size(apoc.coll.intersection(acc, results[index2])) > 0
THEN apoc.coll.union(acc, results[index2])
ELSE acc
END
)) as combinedResult
WITH distinct(combinedResult) as combinedResult
// extra filtering
WITH collect(combinedResult) as allCombinedResults
UNWIND range(0, size(allCombinedResults)-1, 1) as combinedResultIndex
WITH allCombinedResults[combinedResultIndex] as combinedResult, combinedResultIndex, allCombinedResults
WHERE NOT any(x IN range(0,size(allCombinedResults)-1,1)
WHERE x <> combinedResultIndex
AND apoc.coll.containsAll(allCombinedResults[x], combinedResult)
)
RETURN combinedResult
""", param_map={'cutoff': similarity_threshold, 'distance': word_edit_distance})
for row in data:
print(row)
在不涉及太多细节的情况下,我们结合使用文本嵌入和词距来查找图中潜在的重复内容。你可以调整 similarity_threshold 和 word_distance,以找到最佳组合,既能检测到尽可能多的重复,又不会出现过多的误报。不幸的是,实体消歧是一个很难解决的问题,没有完美的解决方案。通过这种方法,我们得到了相当不错的结果,但也有一些误报:
['1963 AFL Draft', '1963 NFL Draft']
['June 14, 2023', 'June 15 2023']
['BTC Halving', 'BTC Halving 2016', 'BTC Halving 2020', 'BTC Halving 2024', 'Bitcoin Halving', 'Bitcoin Halving 2024']
在合并重复节点之前,你可以调整刻度盘,也许还可以添加一些手动异常。
实现自定义检索器
我们已经基于新闻数据集构建了一个知识图谱。现在,让我们检查一下我们的检索器选项。目前,有四种可用的检索器:
- LLMSynonymRetriever 接收查询,并尝试生成关键字和同义词来检索节点(以及连接到这些节点的路径)。
- VectorContextRetriever 根据节点的向量相似性检索节点,并获取连接到这些节点的路径。
- TextToCypherRetriever 使用图存储模式、你的查询和提示模板来生成和执行 Cypher 查询。
- CypherTemplateRetriever 提供一个加密语法模板,由 LLM 填入参数,而不是让 LLM 自由生成任何加密语法语句。
此外,实现自定义解扰器非常简单,这也正是我们要做的。我们的自定义检索器将首先识别输入查询中的实体,然后对每个识别出的实体分别执行 VectorContextRetriever。
首先,我们将定义实体提取模型和提示:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional, List
class Entities(BaseModel):
"""List of named entities in the text such as names of people, organizations, concepts, and locations"""
names: Optional[List[str]]
prompt_template_entities = """
Extract all named entities such as names of people, organizations, concepts, and locations
from the following text:
{text}
"""
现在,我们可以继续实现自定义的捕获器了:
from typing import Any, Optional
from llama_index.core.embeddings import BaseEmbedding
from llama_index.core.retrievers import CustomPGRetriever, VectorContextRetriever
from llama_index.core.vector_stores.types import VectorStore
from llama_index.program.openai import OpenAIPydanticProgram
class MyCustomRetriever(CustomPGRetriever):
"""Custom retriever with entity detection."""
def init(
self,
## vector context retriever params
embed_model: Optional[BaseEmbedding] = None,
vector_store: Optional[VectorStore] = None,
similarity_top_k: int = 4,
path_depth: int = 1,
include_text: bool = True,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
"""Uses any kwargs passed in from class constructor."""
self.entity_extraction = OpenAIPydanticProgram.from_defaults(
output_cls=Entities, prompt_template_str=prompt_template_entities
)
self.vector_retriever = VectorContextRetriever(
self.graph_store,
include_text=self.include_text,
embed_model=embed_model,
similarity_top_k=similarity_top_k,
path_depth=path_depth,
)
def custom_retrieve(self, query_str: str) -> str:
"""Define custom retriever with entity detection.
Could return `str`, `TextNode`, `NodeWithScore`, or a list of those.
"""
entities = self.entity_extraction(text=query_str).names
result_nodes = []
if entities:
print(f"Detected entities: {entities}")
for entity in entities:
result_nodes.extend(self.vector_retriever.retrieve(entity))
else:
result_nodes.extend(self.vector_retriever.retrieve(query_str))
final_text = "\n\n".join(
[n.get_content(metadata_mode="llm") for n in result_nodes]
)
return final_text
MyCustomRetriever 类只有两个方法。你可以使用 init 方法来实例化你将在检索器中使用的任何函数或类。在本例中,我们实例化了实体检测 OpenAI 程序和向量上下文检索器。
在检索过程中会调用 custom_retrieve 方法。在我们的自定义检索器实现中,我们首先会识别文本中的任何相关实体。如果找到任何实体,我们就会对每个实体进行迭代并执行矢量上下文检索器。另一方面,如果没有找到任何实体,我们会将整个输入传递给向量上下文检索器。
正如你所观察到的,你可以通过整合现有的检索器或从头开始,轻松地为你的用例定制检索器,因为你可以使用图存储的 structured_query 方法轻松地执行 Cypher 语句。
问题解答流程
最后,让我们使用自定义检索器来回答一个示例问题。我们需要将检索器传递给 RetrieverQueryEngine:
from llama_index.core.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEngine
custom_sub_retriever = MyCustomRetriever(
index.property_graph_store,
include_text=True,
vector_store=index.vector_store,
embed_model=embed_model
)
query_engine = RetrieverQueryEngine.from_args(
index.as_retriever(sub_retrievers=[custom_sub_retriever]), llm=llm
)
让我们来测试一下:
response = query_engine.query(
"What do you know about Maliek Collins or Darragh O’Brien?"
)
print(str(response))
# Detected entities: ['Maliek Collins', "Darragh O'Brien"]
# Maliek Collins is a defensive tackle who has played for the Dallas Cowboys, Las Vegas Raiders, and Houston Texans. Recently, he signed a two-year contract extension with the Houston Texans worth $23 million, including a $20 million guarantee. This new deal represents a raise from his previous contract, where he earned $17 million with $8.5 million guaranteed. Collins is expected to be a key piece in the Texans' defensive line and fit well into their 4-3 alignment.
# Darragh O’Brien is the Minister for Housing and has been involved in the State’s industrial relations process and the Government. He was recently involved in a debate in the Dáil regarding the pay and working conditions of retained firefighters, which led to a heated exchange and almost resulted in the suspension of the session. O’Brien expressed confidence that the dispute could be resolved and encouraged unions to re-engage with the industrial relations process.
总结
我们已经探索了在 LlamaIndex 中自定义属性图索引的复杂性,重点是实现实体重复数据删除和设计自定义检索方法,以提高 GraphRAG 的准确性。属性图索引允许采用模块化和灵活的方法,使用各种图构造函数和检索器来根据你的需求量身定制实施方案。无论你是首次构建知识图谱,还是针对独特的数据集进行优化,这些可定制的组件都能为你提供强大的工具包。































