使用LiteLLM构建适用于生产级规模的强大LLM 应用程序
LiteLLM 是一种创新型代理,通过提供符合 OpenAI API 规范的统一标准,简化了将各种大型语言模型(LLM)集成到应用程序中的过程。它允许在不同的 LLM 提供商(如 Azure OpenAI、Ollama、OpenAI、Cohere 和 Gemini)之间无缝切换。这种灵活性支持各种用例,包括自定义检索增强生成(RAG)、代理任务和普通聊天交互,提高了部署 LLM 驱动的解决方案的效率和适应性。
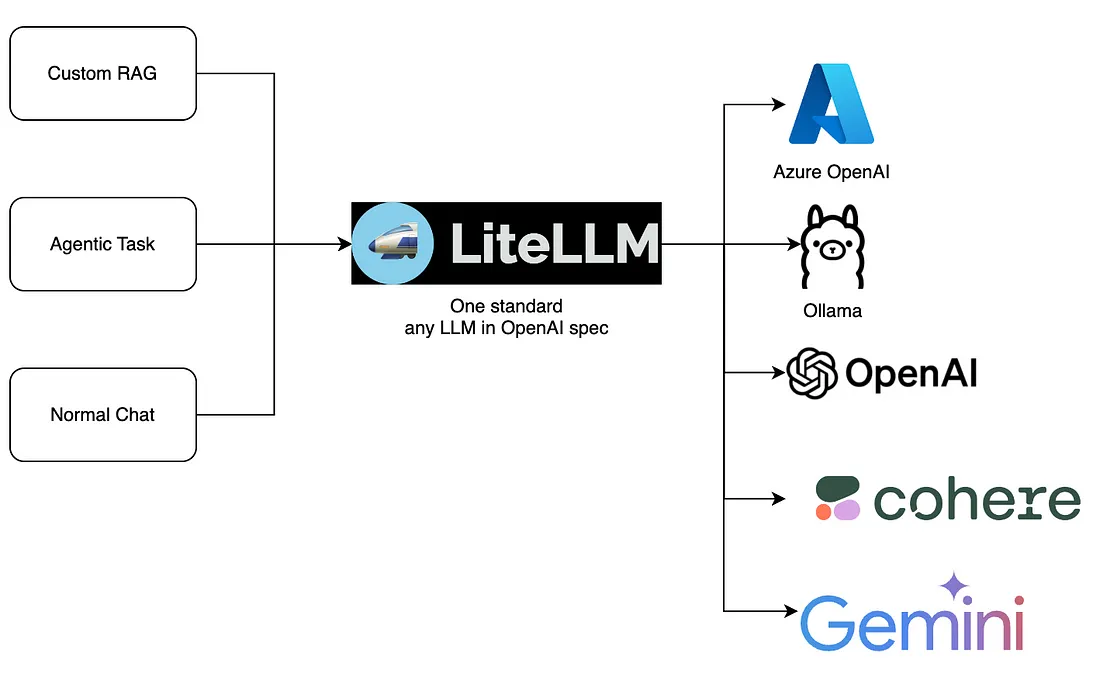
什么是LiteLLM?
LiteLLM是一个Python库,旨在简化各种大型语言模型(LLM)API的集成。它支持众多提供商提供的 100 多种 LLM 服务,使用户能够使用标准化的 OpenAI API 格式与这些模型进行交互。提供商包括 Azure、AWS Bedrock、Anthropic、HuggingFace、Cohere、OpenAI、Ollama 和 Sagemaker 等知名企业。这种广泛的兼容性为用户提供了广泛的语言模型功能,简化了将高级语言模型纳入其应用程序的过程。
什么是 LiteLLM 代理?
LiteLLM Proxy 是 LiteLLM 模型 I/O 库的一个关键组件,旨在对 Azure、Anthropic 和 OpenAI 等各种语言模型服务的 API 调用进行标准化。作为中间件,LiteLLM Proxy 通过提供统一的接口,简化了与多个 LLM API 的交互。它可以管理 API 密钥、处理错误回退、记录请求和响应、跟踪令牌使用和支出情况,并提供缓存和速率限制等功能。此外,它还支持一致的输入/输出格式,对高效的 LLM 应用程序管理至关重要。
如何创建自己的 LiteLLM 代理?
model_list:
- model_name: llama3:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/llama3
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: gemma2:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/gemma2
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: mistral:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/mistral
api_base: http://localhost:11434
运行时执行: litellm - config litellm-config.yml
此 LiteLLM Proxy 配置定义了要使用的模型列表,并指定了每个模型的详细信息。model_list 包括三个模型:llama3:latevs、gemma2:latevs 和 mistral:latevs。每个条目都有 litellm_params,提供 LiteLLM 与这些模型交互所需的参数。模型参数标识了 Ollama 上托管的特定模型版本,而 api_base 参数则设置了引导 API 请求的本地端点 (http://localhost:11434)。这一设置可确保 LiteLLM Proxy 能正确路由和处理这些模型的请求。
如何启动 LiteLLM 控制面板?
为了启动 LiteLLM 控制面板,我们只需对上述配置稍作调整。
model_list:
- model_name: llama3:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/llama3
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: gemma2:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/gemma2
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: mistral:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/mistral
api_base: http://localhost:11434
general_settings:
master_key: "sk-1234" # Your master key for the proxy server. Can use this to send /chat/completion requests etc
database_url: "postgresql://<user>:<password>@localhost:5432/postgres" # Need a postgres database? (Check out Supabase, Neon, etc)
store_model_in_db: true # Allow storing models in db
使用 http://0.0.0.0:4000/ui 登录管理员仪表板,然后会看到下面的内容。
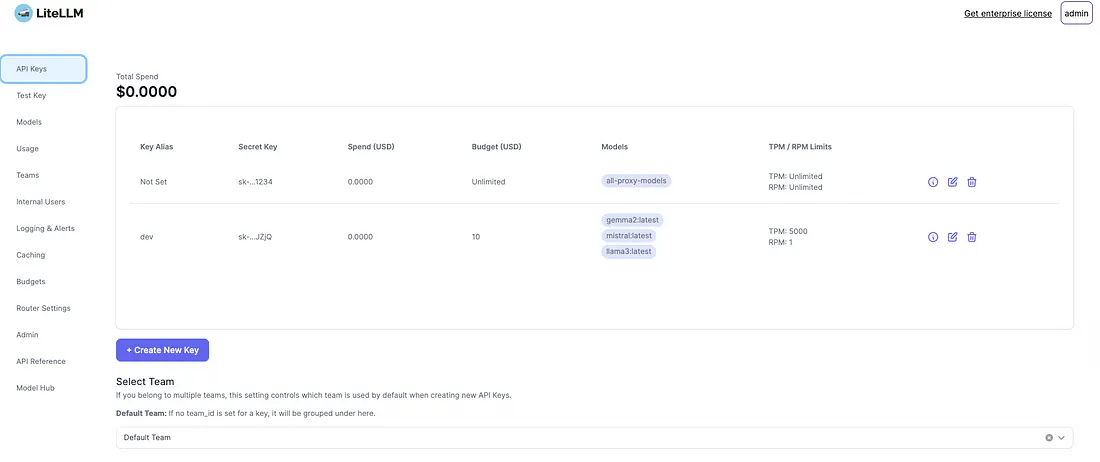
LiteLLM 控制面板的一些重要功能如下。
API 密钥
LiteLLM 的 API 密钥部分允许用户管理其访问密钥,对其使用情况和预算进行详细控制。用户可以创建新密钥、设置别名并指定支出限额。此外,他们还可以为每个密钥分配不同的模型,并定义每分钟令牌数(TPM)和每分钟请求数(RPM)的限制。界面包括设置最大预算和密钥到期时间的选项。这种细粒度控制可确保在通过 LiteLLM 使用各种 LLM 时有效管理资源和成本。
模型
LiteLLM 中的 "模型 "选项卡可对各种语言模型进行全面管理。它允许用户轻松添加、配置和监控模型。用户可以为 llama3:latest 等不同模型设置特定的重试策略,指定 BadRequestError 或 TimeoutError 等各种错误的重试次数。该选项卡还提供分析功能,显示每种模型的每个令牌和异常的平均延迟等指标。此外,它还能进行详细配置,如设置 API 基本 URL、每分钟令牌数(TPM)、每分钟请求数(RPM)以及每个模型的其他参数,从而确保稳健和可定制的模型管理。
路由器设置
LiteLLM 中的 "路由器设置 "选项卡提供了大量选项,用于配置请求的处理和路由方式。在负载平衡下,用户可以设置路由策略、允许的失败次数、失败后的冷却时间、重试次数和超时值。在 "后备 "部分,用户可以设置后备模型,以确保在主模型发生故障时服务的连续性。常规选项卡管理并行请求限制,指定每个 API 密钥的最大并行请求和代理实例的全局并行请求。这些设置可确保在 LLM 应用程序中高效、可靠地处理请求。
有许多功能,但其中一个重要的安全投诉功能是防护栏,下面是我们如何在 LiteLLM 配置中设置默认防护栏。
model_list:
- model_name: llama3:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/llama3
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: gemma2:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/gemma2
api_base: http://localhost:11434
- model_name: mistral:latest
litellm_params:
model: ollama/mistral
api_base: http://localhost:11434
litellm_settings:
guardrails:
- prompt_injection: # your custom name for guardrail
callbacks: [lakera_prompt_injection] # litellm callbacks to use
default_on: true # will run on all llm requests when true
- pii_masking: # your custom name for guardrail
callbacks: [presidio] # use the litellm presidio callback
default_on: false # by default this is off for all requests
- hide_secrets_guard:
callbacks: [hide_secrets]
default_on: false
- your-custom-guardrail
callbacks: [hide_secrets]
default_on: false
给定的 LiteLLM 配置定义了多个防护栏,以确保与大型语言模型进行安全、合规的交互。每个防护栏都指定了一个自定义名称和相关回调,以处理特定任务。
- prompt_injection: 使用默认启用的 lakera_prompt_injection 回调,以防止提示注入攻击。
- pii_masking: 使用 presidio 回调屏蔽个人身份信息(PII),但默认情况下禁用。
- hide_secrets_guard(隐藏秘密保护 使用 hide_secrets 回调,默认情况下也禁用。
- your-custom-guardrail: 自定义防护栏示例,使用 hide_secrets 回调,默认为禁用。
集成和实施
这是一个简单的 RAG,通过 LiteLLM 代理连接到 Azure OpenAI
from llama_index.embeddings.ollama import OllamaEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.azure_openai import AzureOpenAI
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader, ServiceContext, VectorStoreIndex
'''
sample litellm config as below.
model_list:
- model_name: azure-gpt-3.5
model: azure/azure-gpt-3.5 ### MODEL NAME sent to `litellm.completion()` ###
api_base: https://my-endpoint-useeast-mantha-868.openai.azure.com/
api_key: "YOUR_AZURE_API_KEY" # does os.getenv("YOUR_AZURE_API_KEY")
rpm: 6 # [OPTIONAL] Rate limit for this deployment: in requests per minute (rpm)
'''
embed_model = OllamaEmbedding(model_name='mxbai-embed-large:latest', base_url='http://localhost:11434')
llm = AzureOpenAI(
engine="azure-gpt-3.5", # model_name on litellm proxy
temperature=0.0,
azure_endpoint="http://localhost:4000", # litellm proxy endpoint
api_key="sk-DdYGeoO7PoanQYWSP_JZjQ", # litellm proxy API Key
api_version="2023-07-01-preview",
)
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("product_manual_data", required_exts=['.pdf']).load_data()
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm=llm, embed_model=embed_model)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents, service_context=service_context)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("convert the product specification to JSON")
print(response)
使用 Qdrant 混合检索和 LiteLLM 代理 API 定制 RAG
qdrant_ops.py
import json
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient, models
from utils.decorator_utils import execution_time_decorator
class HybridQdrantOperations:
def __init__(self):
self.payload_path = "../data.json"
self.collection_name = "hybrid-multi-stage-queries-collection"
self.DENSE_MODEL_NAME = "snowflake/snowflake-arctic-embed-s"
self.SPARSE_MODEL_NAME = "prithivida/Splade_PP_en_v1"
# collect to our Qdrant Server
self.client = QdrantClient(url="http://localhost:6333", api_key="YOUR_KEY")
self.client.set_model(self.DENSE_MODEL_NAME)
# comment this line to use dense vectors only
self.client.set_sparse_model(self.SPARSE_MODEL_NAME)
self.metadata = []
self.documents = []
def load_data(self):
with open(self.payload_path) as fd:
for line in fd:
obj = json.loads(line)
self.documents.append(obj.pop("description"))
self.metadata.append(obj)
def create_collection(self):
if not self.client.collection_exists(collection_name=f"{self.collection_name}"):
self.client.create_collection(
collection_name=f"{self.collection_name}",
vectors_config=self.client.get_fastembed_vector_params(),
# comment this line to use dense vectors only
sparse_vectors_config=self.client.get_fastembed_sparse_vector_params(on_disk=True),
optimizers_config=models.OptimizersConfigDiff(
default_segment_number=5,
indexing_threshold=0,
),
quantization_config=models.BinaryQuantization(
binary=models.BinaryQuantizationConfig(always_ram=True),
),
shard_number=4
)
@execution_time_decorator
def insert_documents(self):
self.client.add(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
documents=self.documents,
metadata=self.metadata,
parallel=5, # Use all available CPU cores to encode data if the value is 0
)
# self._optimize_collection_after_insert()
@execution_time_decorator
def hybrid_search(self, text: str, top_k: int = 5):
# self.client.query will have filters also if you want to do query on filter data.
search_result = self.client.query(
collection_name=self.collection_name,
query_text=text,
limit=top_k, # 5 the closest results
)
# `search_result` contains found vector ids with similarity scores
# along with the stored payload
# Select and return metadata
metadata = [hit.metadata for hit in search_result]
return metadata
def _optimize_collection_after_insert(self):
self.client.update_collection(
collection_name=f'{self.collection_name}',
optimizer_config=models.OptimizersConfigDiff(indexing_threshold=30000)
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ops = HybridQdrantOperations()
# only run the below for the first time when you newly create collection and want to ingest the data.
ops.load_data()
ops.create_collection()
ops.insert_documents()
# results = ops.hybrid_search(text="What are the gaming companies in bangalore?", top_k=10000)
# print(results)
custom_rag.py
import json
from qdrant_ops import HybridQdrantOperations
from utils.decorator_utils import execution_time_decorator
import requests
class StartupRAG:
def __init__(self, retriever: HybridQdrantOperations = HybridQdrantOperations()):
self.retriever = retriever
def _fetch_context(self, user_query: str = None):
context_retrieved = self.retriever.hybrid_search(text=user_query, top_k=3)
print(f"context_retrieved: {context_retrieved}")
return context_retrieved
@execution_time_decorator
def completion(self, str_or_query: str = None):
context = self._fetch_context(user_query=str_or_query)
rag_prompt_tmpl = (
"given below is the Context information.\n"
"---------------------\n"
f"{json.dumps(context)}\n"
"---------------------\n"
"provided the context information, I want you to think step by step to answer the "
"query in a crisp manner, incase case you don't know the answer say 'I don't know!'.\n"
f"Query: {str_or_query}\n"
"Answer: "
)
llm_response = self._call_litellm(content=rag_prompt_tmpl)
return llm_response
def _call_litellm(self, content: str):
url = "http://0.0.0.0:4000/chat/completions"
payload = {
"model": "ollama/gemma2",
"temperature": 0.8,
"max_tokens": 100,
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"{content}"
}
]
}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json", "Authorization": "Bearer sk-DdYGeoO7PoanQYWSP_JZjQ",}
resp = requests.request("POST", url, json=payload, headers=headers)
return resp.text
if __name__ == "__main__":
rag = StartupRAG()
# Start a loop to continually get input from the user
while True:
# Get a query from the user
user_query = input("Enter your query [type 'bye' to 'exit']: ")
# Check if the user wants to terminate the loop
if user_query.lower() == "bye" or user_query.lower() == "exit":
break
response = rag.completion(str_or_query=user_query)
print(response)
utility.py
import time
from functools import wraps
def execution_time_decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
execution_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"Execution time for {func.__name__}: {execution_time:.6f} seconds")
return result
return wrapper
使用 LiteLLM API:
如果你是应用程序接口狂热者,LiteLLM 提供了大量应用程序接口,你可以使用 http://0.0.0.0:4000 查看这些应用程序接口。
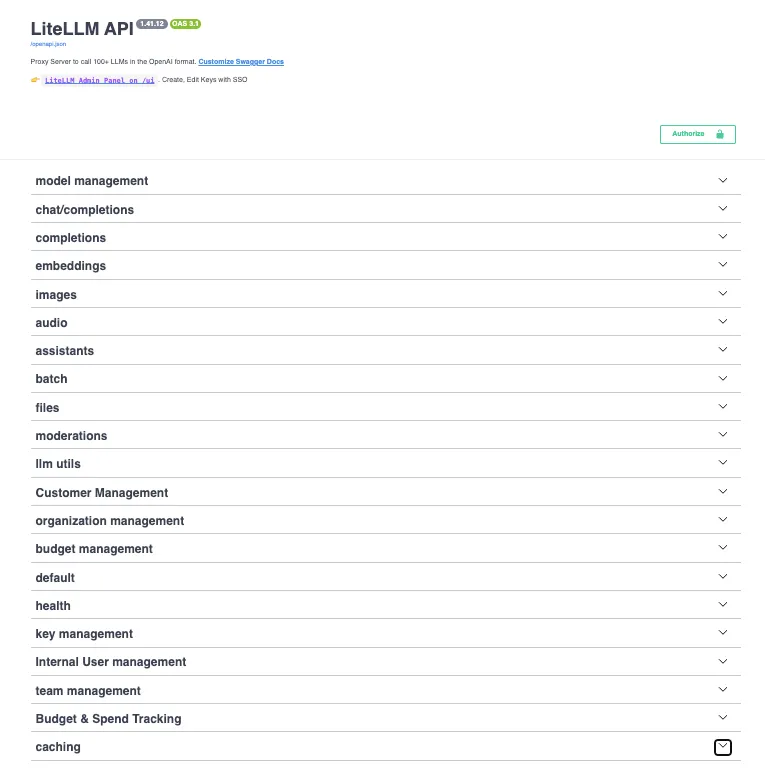
LiteLLM Swagger 界面可显示可用功能和端点的综合列表,便于与 LiteLLM 服务的各个方面进行交互。主要功能包括:
- 模型管理: 管理和配置模型。
- 聊天/完成 处理聊天互动和完成请求。
- 嵌入 处理文本嵌入。
- 图像和音频 管理图片和音频数据。
- 文件和管理 处理文件上传和内容管理。
- 客户和组织管理 管理客户和组织设置。
- 预算和支出跟踪 监控和管理预算。
- 缓存和健康 配置缓存并监控系统健康状况。
- 密钥和团队管理 处理 API 密钥和团队设置。
未来架构
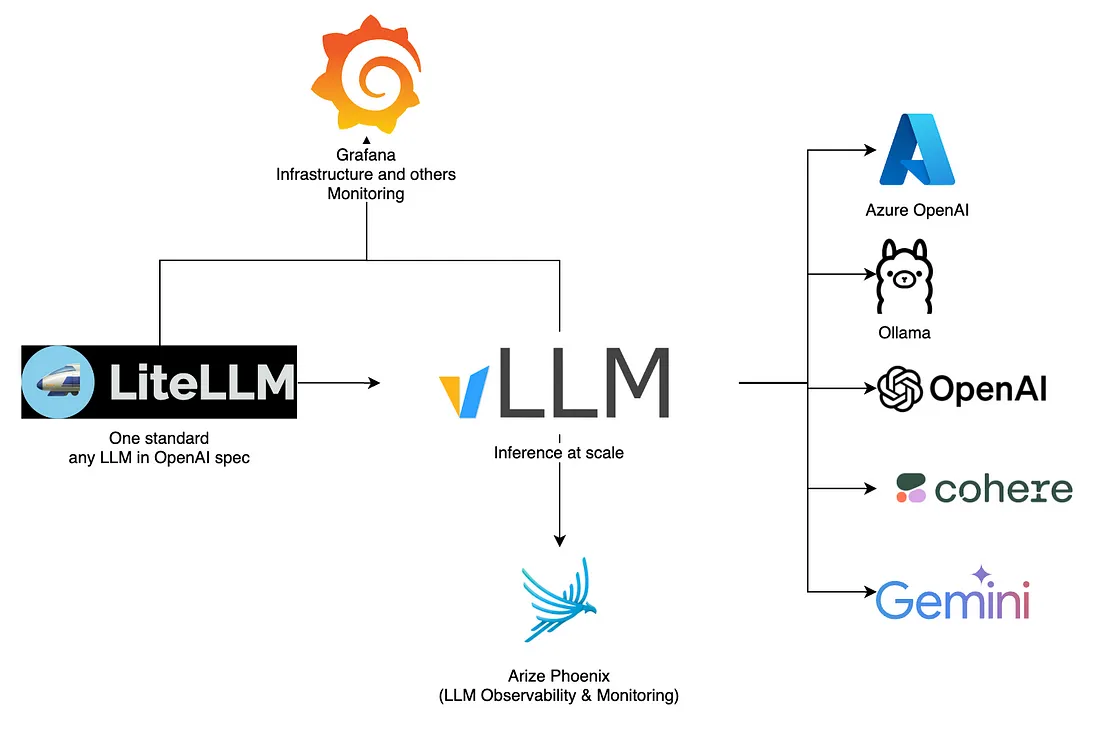
结论
总之,LiteLLM 及其组件(如 LiteLLM Proxy)为将各种大型语言模型集成到你的应用程序中提供了强大的解决方案。该系统能够标准化 API 调用、管理模型,并处理错误处理、缓存和速率限制等交叉问题,从而简化了由 LLM 驱动的服务的开发和部署。LiteLLM拥有详细的模型、路由和防护栏配置选项,可确保与多个LLM提供商进行高效、安全和合规的交互。采用 LiteLLM 可以显著增强语言模型应用的功能和性能。































