使用Celery、Redis 和 Florence 2进行异步机器学习推理
大多数机器学习服务教程都侧重于实时同步服务,这样可以立即响应预测请求。然而,这种方法在流量激增时会很吃力,对于长期运行的任务也不理想。它还需要更强大的机器才能快速响应,而且如果客户端或服务器出现故障,预测结果通常会丢失。
在这篇文中,我们将演示如何使用 Celery 和 Redis 作为异步 Worker 运行机器学习模型。我们将使用 Florence 2 基础模型,这是一个以性能惊人而著称的视觉语言模型。本教程将提供一个最小但功能强大的示例,你可以根据自己的用例进行调整和扩展。
我们解决方案的核心基于 Celery,它是一个 Python 库,为我们实现了客户端/工作逻辑。它允许我们将计算工作分配给多个 Worker,从而提高 ML 推断用例的可扩展性,以应对高负载和不可预测的负载。
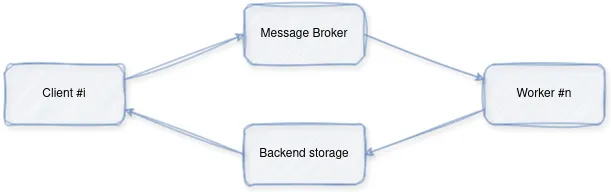
流程如下:
- 客户端向代理管理的队列(在我们的示例中为 Redis)提交带有一些参数的任务。
- 一个 Worker(或多个 Worker)会持续监控队列,并在任务到来时拾取它们。然后执行这些任务,并将结果保存到后端存储中。
- 客户端可以通过轮询后端或订阅任务通道,使用任务的 ID 获取任务结果。
让我们从一个简化的例子开始:
首先,运行 Redis:
docker run -p 6379:6379 redisp 6379:6379 redis
以下是 Worker 代码:
from celery import Celery
# Configure Celery to use Redis as the broker and backend
app = Celery(
"tasks", broker="redis://localhost:6379/0", backend="redis://localhost:6379/0"
)
# Define a simple task
@app.task
def add(x, y):
return x + y
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.worker_main(["worker", "--loglevel=info"])
以及客户端代码:
from celery import Celery
app = Celery("tasks", broker="redis://localhost:6379/0", backend="redis://localhost:6379/0")
print(f"{app.control.inspect().active()=}")
task_name = "tasks.add"
add = app.signature(task_name)
print("Gotten Task")
# Send a task to the worker
result = add.delay(4, 6)
print("Waiting for Task")
result.wait()
# Get the result
print(f"Result: {result.result}")
这样就得到了我们期望的结果: “结果:10
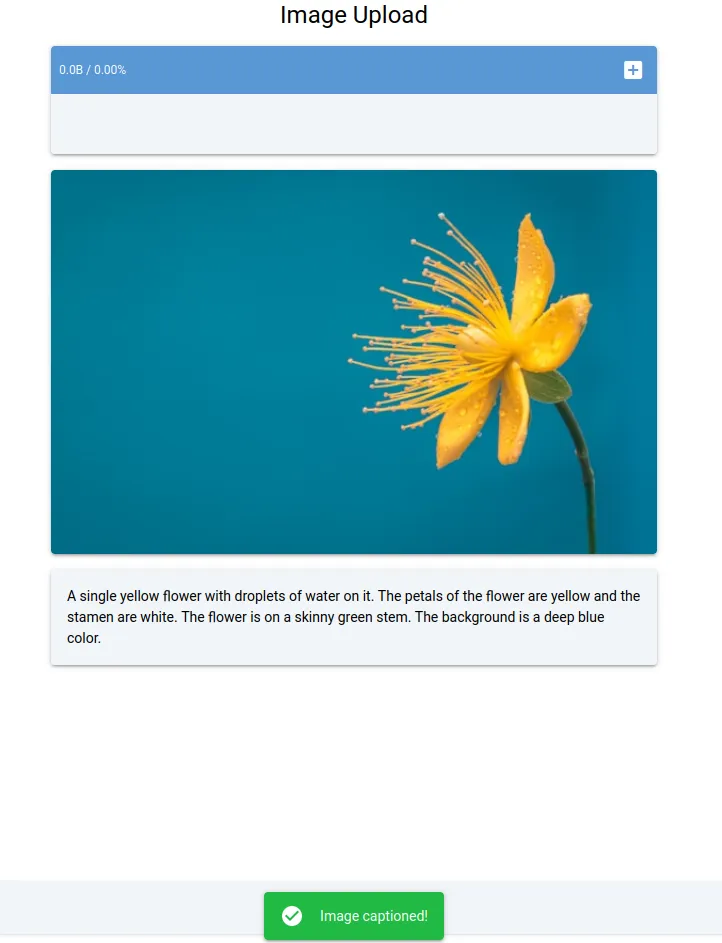
现在,让我们进入真正的用例: 服务Florence 2。
我们将构建一个多容器图像字幕应用程序,使用 Redis 进行任务队列,使用 Celery 进行任务分配,并使用本地卷或谷歌云存储进行潜在图像存储。该应用的设计包含几个核心组件:模型推理、任务分配、客户端交互和文件存储。
架构概述:
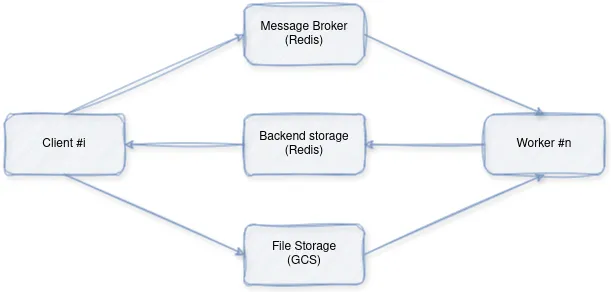
- 客户端: 通过代理向工作站发送图像字幕请求。
- 工作站:接收请求、下载图像、使用预训练模型执行推理并返回结果。
- Redis:充当消息代理,促进客户端与 Worker 之间的通信。
- 文件存储: 图像文件的临时存储
组件分解
1. 模型推理(model.py):
- 依赖关系与初始化:
import os
from io import BytesIO
import requests
from google.cloud import storage
from loguru import logger
from modeling_florence2 import Florence2ForConditionalGeneration
from PIL import Image
from processing_florence2 import Florence2Processor
model = Florence2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"microsoft/Florence-2-base-ft"
)
processor = Florence2Processor.from_pretrained("microsoft/Florence-2-base-ft")
- 导入图像处理、网络请求、谷歌云存储交互和日志记录所需的库。
- 初始化预训练的 Florence-2 模型和处理器,以生成图像标题。
- 图像下载(download_image):
def download_image(url):
if url.startswith("http://") or url.startswith("https://"):
# Handle HTTP/HTTPS URLs
# ... (code to download image from URL) ...
elif url.startswith("gs://"):
# Handle Google Cloud Storage paths
# ... (code to download image from GCS) ...
else:
# Handle local file paths
# ... (code to open image from local path) ...
- 从提供的 URL 下载图片。
- 支持 HTTP/HTTPS URL、谷歌云存储路径 (gs://) 和本地文件路径。
- 推理执行(run_inference):
def run_inference(url, task_prompt):
# ... (code to download image using download_image function) ...
try:
# ... (code to open and process the image) ...
inputs = processor(text=task_prompt, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
except ValueError:
# ... (error handling) ...
# ... (code to generate captions using the model) ...
generated_ids = model.generate(
input_ids=inputs["input_ids"],
pixel_values=inputs["pixel_values"],
# ... (model generation parameters) ...
)
# ... (code to decode generated captions) ...
generated_text = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=False)[0]
# ... (code to post-process generated captions) ...
parsed_answer = processor.post_process_generation(
generated_text, task=task_prompt, image_size=(image.width, image.height)
)
return parsed_answer
协调图像字幕处理过程:
- 使用 download_image 下载图像。
- 为模型准备图像和任务提示。
- 使用加载的 Florence-2 模型生成标题。
- 对生成的标题进行解码和后处理。
- 返回最终字幕。
2. 任务分配 (worker.py):
- Celery 设置:
import os
from celery import Celery
# ... other imports ...
# Get Redis URL from environment variable or use default
REDIS_URL = os.getenv("REDIS_URL", "redis://localhost:6379/0")
# Configure Celery to use Redis as the broker and backend
app = Celery("tasks", broker=REDIS_URL, backend=REDIS_URL)
# ... (Celery configurations) ...
- 设置 Celery 使用 Redis 作为任务分发的消息代理。
- 任务定义(inference_task):
@app.task(bind=True, max_retries=3)
def inference_task(self, url, task_prompt):
# ... (logging and error handling) ...
return run_inference(url, task_prompt)
- 定义 Celery Worker 将执行的 Inference_task 任务。
- 该任务调用 model.py 中的 run_inference 函数。
- 工作者执行:
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.worker_main(["worker", "--loglevel=info", "--pool=solo"])
- 启动 Celery Worker,监听并执行任务。
3. 客户端交互(client.py):
- Celery 连接:
import os
from celery import Celery
# Get Redis URL from environment variable or use default
REDIS_URL = os.getenv("REDIS_URL", "redis://localhost:6379/0")
# Configure Celery to use Redis as the broker and backend
app = Celery("tasks", broker=REDIS_URL, backend=REDIS_URL)
- 使用 Redis 作为消息代理,建立与 Celery 的连接。
- 任务提交(send_inference_task):
def send_inference_task(url, task_prompt):
task = inference_task.delay(url, task_prompt)
print(f"Task sent with ID: {task.id}")
# Wait for the result
result = task.get(timeout=120)
return result
- 向 Celery Worker 发送图像标题任务(inference_task)。
- 等待 Worker 完成任务并获取结果。
Docker 集成(docker-compose.yml):
- 使用 Docker Compose 定义多容器设置
- redis: 运行 Redis 服务器进行消息中介。
- model: 构建并部署模型推理工作者。
- app: 构建并部署客户端应用程序。
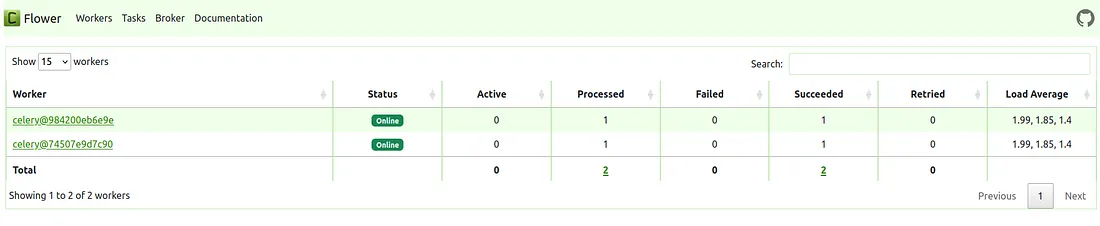
- flower: 运行基于网络的 Celery 任务监控工具。
你可以使用:
docker-compose up
就是这样!我们刚刚探索了使用 Celery、Redis 和 Florence 2 构建异步机器学习推理系统的综合指南。本教程演示了如何有效地使用 Celery 进行任务分配,使用 Redis 进行消息中介,以及使用 Florence 2 进行图像标注。通过采用异步工作流,你可以处理大量请求、提高性能并增强 ML 推断应用程序的整体弹性。通过所提供的 Docker Compose 设置,你只需一条命令就能独立运行整个系统。































