构建智能RAG:Azure实现图像理解与分层文档分析
检索增强生成(RAG)模型的出现是自然语言处理(NLP)领域的一个重要里程碑。这些模型结合了信息检索和生成语言模型的强大功能,不仅能提供准确的答案,还能丰富语境。然而,随着数字世界的扩展超越了文本数据,将图像理解和分层文档结构分析纳入 RAG 系统变得越来越重要。本文将探讨这两个要素如何显著增强 RAG 模型的功能。
了解 RAG 模型
在深入探讨图像理解和文档分析的细微差别之前,让我们先简要谈谈 RAG 模型的本质。这些系统的工作原理是首先从庞大的语料库中检索相关文档,然后使用生成模型将信息合成为一致的响应。检索部分可确保模型获得准确的最新信息,而生成部分则可创建类似人类的文本。
图像理解与结构分析
传统 RAG 模型的最大局限之一就是无法理解和解释视觉数据。在一个图像与文本信息无处不在的世界里,这代表了模型在理解能力上的巨大差距。文档不仅仅是一串文字;它们有结构--章节、小节、段落和列表--所有这些都传达了语义的重要性。传统的 RAG 模型通常会忽略这种层次结构,从而可能无法理解文档的全部含义。
为了弥补这一缺陷,可以利用计算机视觉(CV)功能来增强 RAG 模型。这包括集成图像识别和理解模块,这些模块可以分析视觉数据、提取相关信息,并将其转换为 RAG 模型可以处理的文本格式。纳入分层文档结构分析涉及教会 RAG 模型识别和解释文档的底层结构。
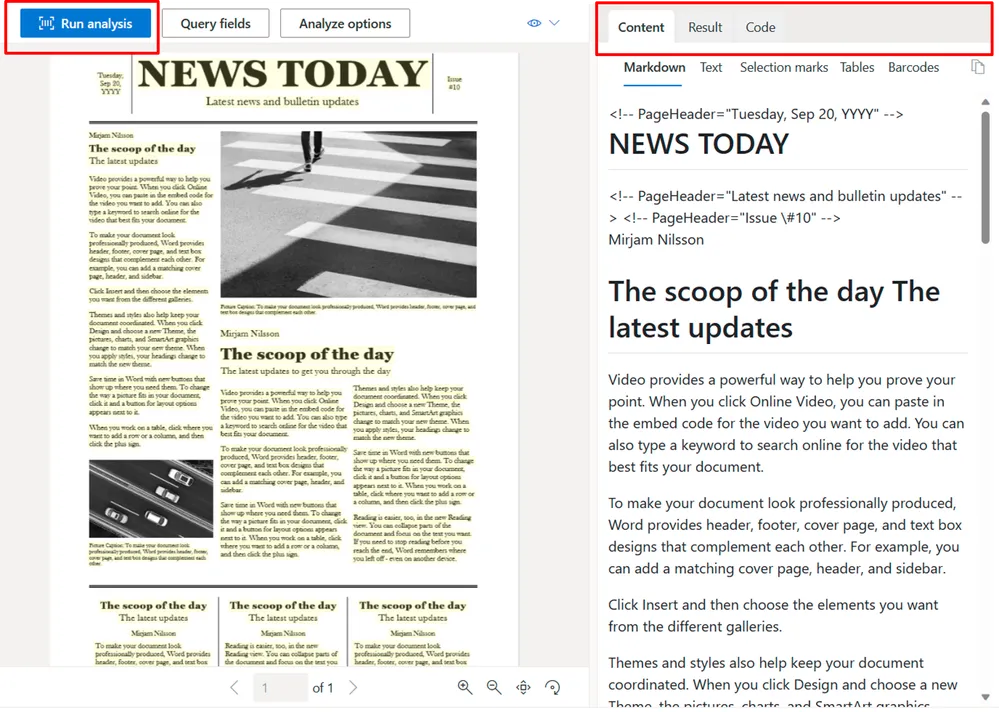
实施
- 视觉特征提取: 使用预先训练好的神经网络来识别图像中的物体、场景和活动。
- 视觉语义: 开发能够理解视觉内容上下文和语义的算法。
- 多模态数据融合: 将提取的视觉信息与文本数据相结合,为 RAG 系统创建多模态语境。
- 结构识别: 实施算法来识别文档中的不同层次,如标题、小标题和要点。
- 语义角色标签: 为文档的不同部分分配语义角色,了解每个部分的目的。
- 结构感知检索: 通过考虑文档的分层结构来增强检索过程,确保使用最相关的部分进行生成。
在本文中,我们将探讨如何使用 Azure Document Intelligence、LangChain 和 Azure OpenAI 实现这一功能。
前提条件
在实施之前,我们需要一些先决条件:
- 已部署 GPT-4-Vision-Preview 模型
- 已部署 GPT-4-1106 预览模型
- 已部署 text-ada-embedding 模型
- 已部署 Azure 文档智能
让我们导入所需的库。
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv('azure.env')
from langchain import hub
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
#from langchain_community.document_loaders import AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader
from doc_intelligence import AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader
from langchain_openai import AzureOpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.schema import StrOutputParser
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain.text_splitter import MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores.azuresearch import AzureSearch
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import DocumentAnalysisFeature
现在,我们要在 LangChain 文档加载器之上编写一些自定义函数,以帮助我们加载 PDF 文档。我们要做的第一件事就是使用 Azure Document Intelligence,它具有将图像转换为 Markdown 格式的强大功能。让我们使用相同的功能。
import logging
from typing import Any, Iterator, List, Optional
import os
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_community.document_loaders.base import BaseLoader
from langchain_community.document_loaders.base import BaseBlobParser
from langchain_community.document_loaders.blob_loaders import Blob
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader(BaseLoader):
"""Loads a PDF with Azure Document Intelligence"""
def __init__(
self,
api_endpoint: str,
api_key: str,
file_path: Optional[str] = None,
url_path: Optional[str] = None,
api_version: Optional[str] = None,
api_model: str = "prebuilt-layout",
mode: str = "markdown",
*,
analysis_features: Optional[List[str]] = None,
) -> None:
"""
Initialize the object for file processing with Azure Document Intelligence
(formerly Form Recognizer).
This constructor initializes a AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceParser object to be
used for parsing files using the Azure Document Intelligence API. The load
method generates Documents whose content representations are determined by the
mode parameter.
Parameters:
-----------
api_endpoint: str
The API endpoint to use for DocumentIntelligenceClient construction.
api_key: str
The API key to use for DocumentIntelligenceClient construction.
file_path : Optional[str]
The path to the file that needs to be loaded.
Either file_path or url_path must be specified.
url_path : Optional[str]
The URL to the file that needs to be loaded.
Either file_path or url_path must be specified.
api_version: Optional[str]
The API version for DocumentIntelligenceClient. Setting None to use
the default value from `azure-ai-documentintelligence` package.
api_model: str
Unique document model name. Default value is "prebuilt-layout".
Note that overriding this default value may result in unsupported
behavior.
mode: Optional[str]
The type of content representation of the generated Documents.
Use either "single", "page", or "markdown". Default value is "markdown".
analysis_features: Optional[List[str]]
List of optional analysis features, each feature should be passed
as a str that conforms to the enum `DocumentAnalysisFeature` in
`azure-ai-documentintelligence` package. Default value is None.
Examples:
---------
>>> obj = AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader(
... file_path="path/to/file",
... api_endpoint="https://endpoint.azure.com",
... api_key="APIKEY",
... api_version="2023-10-31-preview",
... api_model="prebuilt-layout",
... mode="markdown"
... )
"""
assert (
file_path is not None or url_path is not None
), "file_path or url_path must be provided"
self.file_path = file_path
self.url_path = url_path
self.parser = AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceParser(
api_endpoint=api_endpoint,
api_key=api_key,
api_version=api_version,
api_model=api_model,
mode=mode,
analysis_features=analysis_features,
)
def lazy_load(
self,
) -> Iterator[Document]:
"""Lazy load given path as pages."""
if self.file_path is not None:
yield from self.parser.parse(self.file_path)
else:
yield from self.parser.parse_url(self.url_path)
现在我们来定义文档解析器。
class AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceParser(BaseBlobParser):
"""Loads a PDF with Azure Document Intelligence
(formerly Forms Recognizer)."""
def __init__(
self,
api_endpoint: str,
api_key: str,
api_version: Optional[str] = None,
api_model: str = "prebuilt-layout",
mode: str = "markdown",
analysis_features: Optional[List[str]] = None,
):
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import DocumentAnalysisFeature
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
kwargs = {}
if api_version is not None:
kwargs["api_version"] = api_version
if analysis_features is not None:
_SUPPORTED_FEATURES = [
DocumentAnalysisFeature.OCR_HIGH_RESOLUTION,
]
analysis_features = [
DocumentAnalysisFeature(feature) for feature in analysis_features
]
if any(
[feature not in _SUPPORTED_FEATURES for feature in analysis_features]
):
logger.warning(
f"The current supported features are: "
f"{[f.value for f in _SUPPORTED_FEATURES]}. "
"Using other features may result in unexpected behavior."
)
self.client = DocumentIntelligenceClient(
endpoint=api_endpoint,
credential=AzureKeyCredential(api_key),
headers={"x-ms-useragent": "langchain-parser/1.0.0"},
features=analysis_features,
**kwargs,
)
self.api_model = api_model
self.mode = mode
assert self.mode in ["single", "page", "markdown"]
def _generate_docs_page(self, result: Any) -> Iterator[Document]:
for p in result.pages:
content = " ".join([line.content for line in p.lines])
d = Document(
page_content=content,
metadata={
"page": p.page_number,
},
)
yield d
def _generate_docs_single(self, file_path: str, result: Any) -> Iterator[Document]:
md_content = include_figure_in_md(file_path, result)
yield Document(page_content=md_content, metadata={})
def lazy_parse(self, file_path: str) -> Iterator[Document]:
"""Lazily parse the blob."""
blob = Blob.from_path(file_path)
with blob.as_bytes_io() as file_obj:
poller = self.client.begin_analyze_document(
self.api_model,
file_obj,
content_type="application/octet-stream",
output_content_format="markdown" if self.mode == "markdown" else "text",
)
result = poller.result()
if self.mode in ["single", "markdown"]:
yield from self._generate_docs_single(file_path, result)
elif self.mode in ["page"]:
yield from self._generate_docs_page(result)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid mode: {self.mode}")
def parse_url(self, url: str) -> Iterator[Document]:
from azure.ai.documentintelligence.models import AnalyzeDocumentRequest
poller = self.client.begin_analyze_document(
self.api_model,
AnalyzeDocumentRequest(url_source=url),
# content_type="application/octet-stream",
output_content_format="markdown" if self.mode == "markdown" else "text",
)
result = poller.result()
if self.mode in ["single", "markdown"]:
yield from self._generate_docs_single(result)
elif self.mode in ["page"]:
yield from self._generate_docs_page(result)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid mode: {self.mode}")
如果你看看这个 LangChain 文档解析器,我在其中加入了一个名为 include_figure_in_md 的方法。该方法会浏览标记符内容并查找所有数字,然后用相同的描述替换每个数字。
在此之前,请让我们编写一些实用方法,帮助你从 PDF/Image 文档中裁剪图片。
from PIL import Image
import fitz # PyMuPDF
import mimetypes
import base64
from mimetypes import guess_type
# Function to encode a local image into data URL
def local_image_to_data_url(image_path):
# Guess the MIME type of the image based on the file extension
mime_type, _ = guess_type(image_path)
if mime_type is None:
mime_type = 'application/octet-stream' # Default MIME type if none is found
# Read and encode the image file
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
base64_encoded_data = base64.b64encode(image_file.read()).decode('utf-8')
# Construct the data URL
return f_"data:{mime_type};base64,{base64_encoded_data}"
def crop_image_from_image(image_path, page_number, bounding_box):
"""
Crops an image based on a bounding box.
:param image_path: Path to the image file.
:param page_number: The page number of the image to crop (for TIFF format).
:param bounding_box: A tuple of (left, upper, right, lower) coordinates for the bounding box.
:return: A cropped image.
:rtype: PIL.Image.Image
"""
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
if img.format == "TIFF":
# Open the TIFF image
img.seek(page_number)
img = img.copy()
# The bounding box is expected to be in the format (left, upper, right, lower).
cropped_image = img.crop(bounding_box)
return cropped_image
def crop_image_from_pdf_page(pdf_path, page_number, bounding_box):
"""
Crops a region from a given page in a PDF and returns it as an image.
:param pdf_path: Path to the PDF file.
:param page_number: The page number to crop from (0-indexed).
:param bounding_box: A tuple of (x0, y0, x1, y1) coordinates for the bounding box.
:return: A PIL Image of the cropped area.
"""
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
page = doc.load_page(page_number)
# Cropping the page. The rect requires the coordinates in the format (x0, y0, x1, y1).
bbx = [x * 72 for x in bounding_box]
rect = fitz.Rect(bbx)
pix = page.get_pixmap(matrix=fitz.Matrix(300/72, 300/72), clip=rect)
img = Image.frombytes("RGB", [pix.width, pix.height], pix.samples)
doc.close()
return img
def crop_image_from_file(file_path, page_number, bounding_box):
"""
Crop an image from a file.
Args:
file_path (str): The path to the file.
page_number (int): The page number (for PDF and TIFF files, 0-indexed).
bounding_box (tuple): The bounding box coordinates in the format (x0, y0, x1, y1).
Returns:
A PIL Image of the cropped area.
"""
mime_type = mimetypes.guess_type(file_path)[0]
if mime_type == "application/pdf":
return crop_image_from_pdf_page(file_path, page_number, bounding_box)
else:
return crop_image_from_image(file_path, page_number, bounding_box)
接下来,我们将编写一个方法,将图像传递给 GPT-4-Vision 模型,并获取该图像的描述。
from openai import AzureOpenAI
aoai_api_base = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
aoai_api_key= os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY")
aoai_deployment_name = 'gpt-4-vision' # your model deployment name for GPT-4V
aoai_api_version = '2024-02-15-preview' # this might change in the future
MAX_TOKENS = 2000
def understand_image_with_gptv(image_path, caption):
"""
Generates a description for an image using the GPT-4V model.
Parameters:
- api_base (str): The base URL of the API.
- api_key (str): The API key for authentication.
- deployment_name (str): The name of the deployment.
- api_version (str): The version of the API.
- image_path (str): The path to the image file.
- caption (str): The caption for the image.
Returns:
- img_description (str): The generated description for the image.
"""
client = AzureOpenAI(
api_key=aoai_api_key,
api_version=aoai_api_version,
base_url=f"{aoai_api_base}/openai/deployments/{aoai_deployment_name}"
)
data_url = local_image_to_data_url(image_path)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=aoai_deployment_name,
messages=[
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ "role": "user", "content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": f"Describe this image (note: it has image caption: {caption}):" if caption else "Describe this image:"
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": data_url
}
}
] }
],
max_tokens=2000
)
img_description = response.choices[0].message.content
return img_description
现在,一旦我们设置了实用程序方法,就可以直接导入文档智能加载器并加载文档了。
from langchain_community.document_loaders import AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader
loader = AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader(file_path='sample.pdf',
api_key = os.getenv("AZURE_DOCUMENT_INTELLIGENCE_KEY"),
api_endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_DOCUMENT_INTELLIGENCE_ENDPOINT"),
api_model="prebuilt-layout",
api_version="2024-02-29-preview",
mode='markdown',
analysis_features = [DocumentAnalysisFeature.OCR_HIGH_RESOLUTION])
docs = loader.load()
语义分块是自然语言处理中使用的一种强大技术,它将大段文本分解成较小的、主题一致的片段或 “块”,这些片段或 “块 ”在语义上是一致的。语义分块的主要目的是捕捉和保留文本的内在含义,使每个分块尽可能多地包含独立的语义信息。这一过程对于嵌入模型和检索增强生成(RAG)等各种语言模型应用至关重要,因为它有助于克服处理长文本序列时的局限性。通过确保输入语言模型(LLM)的数据在主题和上下文上的一致性,语义分块增强了模型解释和生成相关准确响应的能力。
此外,语义分块还能检索与用户意图密切相关的信息,从而减少噪音并保持语义的完整性,从而提高矢量数据库的信息检索效率。从本质上讲,语义分块是连接大量文本数据和高级语言模型有效处理能力的桥梁,是高效、有意义的自然语言理解和生成的基石。
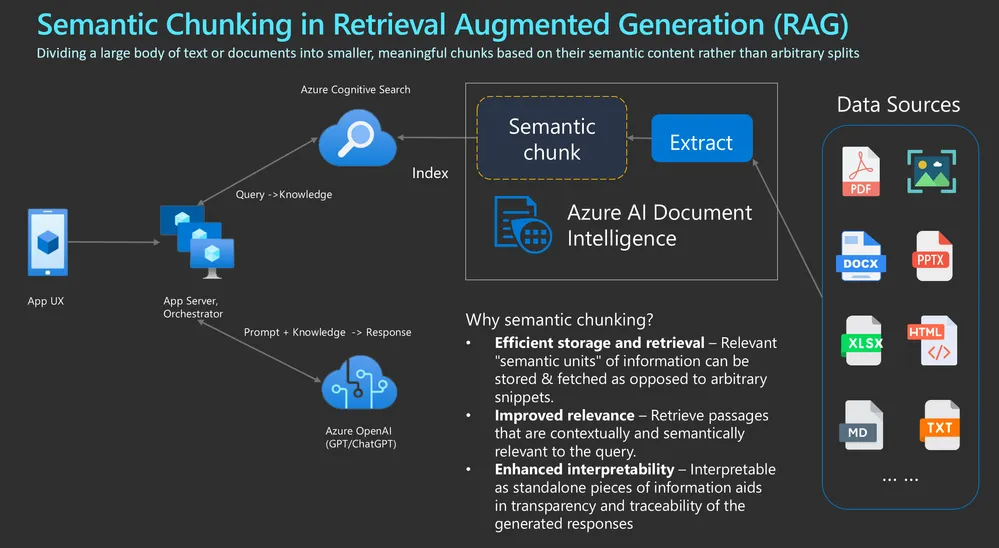
让我们看看 Markdown Header Splitter 如何根据标题分割文档。
# Split the document into chunks base on markdown headers.
headers_to_split_on = [
("#", "Header 1"),
("##", "Header 2"),
("###", "Header 3"),
("####", "Header 4"),
("#####", "Header 5"),
("######", "Header 6"),
("#######", "Header 7"),
("########", "Header 8")
]
text_splitter = MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter(headers_to_split_on=headers_to_split_on)
docs_string = docs[0].page_content
docs_result = text_splitter.split_text(docs_string)
print("Length of splits: " + str(len(docs_result)))
让我们初始化 Azure OpenAI GPT 和 Azure OpenAI Embedding 的模型。
from langchain_openai import AzureOpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
from langchain import hub
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(api_key = os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"],
api_version = "2023-12-01-preview",
azure_endpoint = os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"],
model= "gpt-4-1106-preview",
streaming=True)
aoai_embeddings = AzureOpenAIEmbeddings(
api_key=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"),
azure_deployment="text-embedding-ada-002",
openai_api_version="2023-12-01-preview",
azure_endpoint =os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"]
)
现在,让我们创建一个索引,并将嵌入数据存储到 FAISS 中。
# Return the retrieved documents or certain source metadata from the documents
from operator import itemgetter
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnableMap
index = await FAISS.afrom_documents(documents=docs_result,
embedding=aoai_embeddings)
现在,让我们来创建 RAG Chain。
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
retriever_base = index.as_retriever(search_type="similarity",search_kwargs = {"k" : 5})
rag_chain_from_docs = (
{
"context": lambda input: format_docs(input["documents"]),
"question": itemgetter("question"),
}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
rag_chain_with_source = RunnableMap(
{"documents": retriever_base, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
) | {
"documents": lambda input: [doc.metadata for doc in input["documents"]],
"answer": rag_chain_from_docs,
}
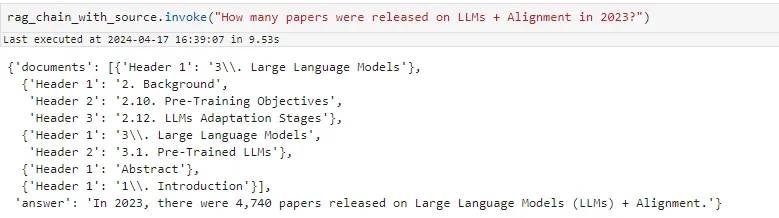
现在让我们付诸行动,以下面的 PDF 为例,向 Plot 提出问题。
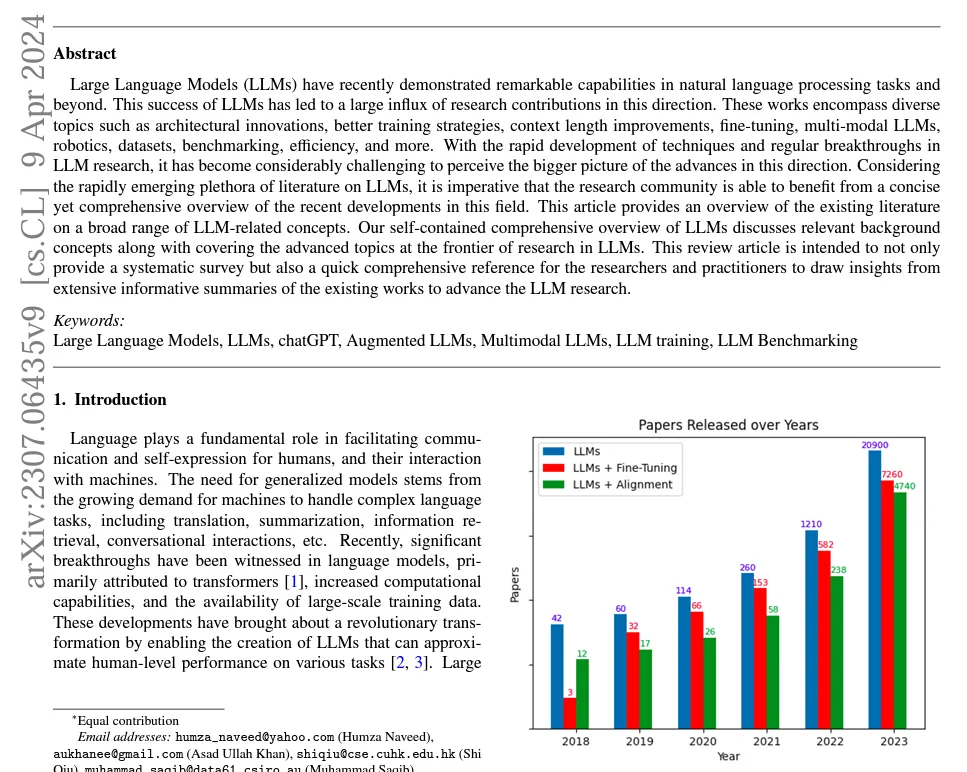
在此,我将从本页的情节中提出一个问题。正如你所看到的,我得到了正确的回答,同时还引用了引文......