构建实时语音助手:结合FastAPI、Groq和OpenAI TTS
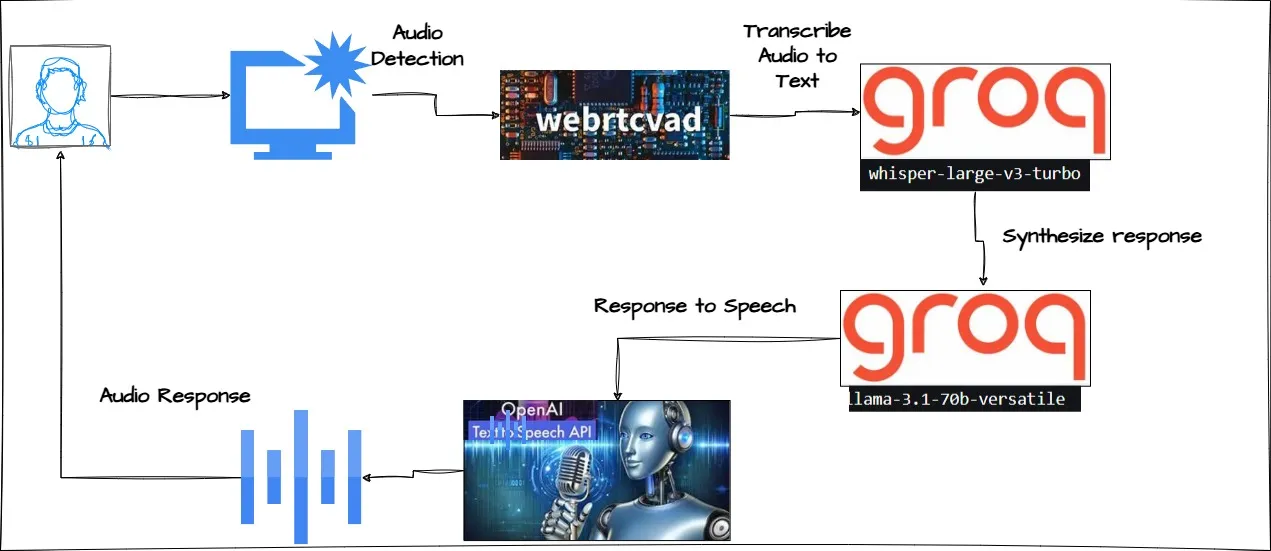
简介
在本文中,我将向你介绍如何构建一个复杂的语音聊天应用程序,该程序结合了实时音频处理、语音识别、自然语言处理和文本到语音合成技术。该应用程序使用FastAPI作为后端,并整合了多种AI服务,以创建一个流畅的基于语音的交互系统。
技术架构
核心技术
- FastAPI:一个用于使用Python构建API的现代、快速的Web框架
- WebSocket:用于实时双向通信
- Groq API:用于语音转文本和聊天补全
- OpenAI API:用于文本转语音合成
- 自定义语音检测:用于实时语音活动检测
处理流程
我们的应用程序实现了一个复杂的处理流程:
语音活动检测
系统持续监控音频输入中的语音活动,有效管理音频流。语音活动检测(VAD)在我们的实时语音聊天应用程序中是一个关键组件。它负责区分音频流中的语音段和非语音段,使应用程序能够仅处理有意义的语音输入。
语音检测的工作原理
基于帧的分析
系统以小的帧(通常每个10-30毫秒)处理音频,以实时判断语音活动。每个帧都会分析以下方面:
- 能量水平
- 频率特性
- 过零率
- 频谱特征
静音检测
系统:
- 跟踪静音时段
- 使用可配置的阈值(1.5秒)
- 维护运行中的音频数据缓冲区
缓冲区管理
关键方面:
- 动态缓冲区大小调整
- 高效的内存管理
- 实时处理能力
voice_detector = VoiceDetector()
voice_detected = voice_detector.detect_voice(data)
语音转文本(Groq Whisper)
音频通过Groq API的Whisper模型进行处理,以实现准确的转录。
async def transcribe_audio(audio_data: bytes):
"""Transcribe audio using Groq's Whisper model"""
temp_wav = None
try:
# Create a unique temporary file
temp_wav = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix='.wav', delete=False)
wav_path = temp_wav.name
temp_wav.close() # Close the file handle immediately
# Write the WAV file
with wave.open(wav_path, 'wb') as wav_file:
wav_file.setnchannels(1) # Mono
wav_file.setsampwidth(2) # 2 bytes per sample (16-bit)
wav_file.setframerate(16000) # 16kHz
wav_file.writeframes(audio_data)
# Transcribe using Groq
with open(wav_path, 'rb') as audio_file:
response = await groq_client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-large-v3-turbo",
file=audio_file,
response_format="text"
)
return response
响应生成
使用Groq API,将转录的文本通过llama-3.1–70b-versatile模型进行处理,以合成针对所提供指令的响应。
async def get_chat_response(text: str):
"""Get chat response from Groq"""
try:
response = await groq_client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.1-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please provide a clear, concise, and accurate response."},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
],
temperature=0,
max_tokens=500
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Chat response error: {str(e)}")
return None
文本转语音(OpenAI)
系统使用OpenAI的文本转语音(TTS)服务将响应转换回语音。
async def generate_speech(text: str):
"""Generate speech using OpenAI TTS"""
try:
response = await openai_client.audio.speech.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy",
input=text
)
# Get the speech data directly from the response
# No need to await response.read() as the response is already the audio data
return response.content
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Speech generation error: {str(e)}")
return None
关键功能
实时处理
该应用程序使用WebSocket连接进行实时音频流和处理。这实现了以下功能:
- 即时语音活动检测
- 连续音频缓冲
- 动态静音检测
- 实时响应生成
智能音频管理
max_silence_duration = 1.5 # seconds
frames_per_second = 1000 / voice_detector.frame_duration
系统智能地管理音频缓冲和静音检测,以提供自然的对话流程。
实现细节
WebSocket处理器
WebSocket端点管理整个对话流程:
- 接受传入的音频流
- 缓冲音频数据
- 检测语音活动
- 处理完整的语句
- 生成并返回响应
音频处理
系统处理音频时非常注重以下方面:
- 适当的文件处理
- 内存管理
- 资源清理
- 格式转换
错误处理和日志记录
全面的错误处理和日志记录确保系统可靠性和易于调试。
实施的最佳实践
异步处理
- 使用FastAPI的异步功能
- 实现高效的资源管理
- 处理并发连接
错误处理
- 全面的try-except块
- 适当的资源清理
- 详细的错误日志记录
配置管理
- 环境变量处理
- 外部配置文件
- 安全的API密钥管理
代码实现
代码文件夹结构:
project_root/
├── main.py # 主FastAPI应用程序
├── config.py # 配置设置
├── requirements.txt # Python依赖项
│
├── static/ # 静态文件目录
│ ├── css/
│ ├── js/
│ └── assets/
│
├── templates/ # Jinja2模板
│ └── index.html # 主模板文件
│
├── voice_modules/ # 语音处理模块
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── realtime_voice_detection.py # 语音检测实现
│
└── README.md # 项目文档
此结构遵循FastAPI推荐的组织Web应用程序的最佳实践,具有以下特点:
- 关注点清晰分离
- 模块化组织
- 易于维护和扩展
- 安全的配置管理
设置API密钥
OpenAI API密钥和Groq API密钥在config.py中设置为键值对。
config = {"OPENAI_API_KEY":"...","GROQ_API_KEY":"..."}FastAPI实现
在FastAPI应用中,静态文件夹是一个至关重要的部分,它提供了一种结构化的方式来管理和提供静态资源。通过组织CSS、JavaScript和其他媒体文件,开发人员可以创建一个响应迅速且视觉吸引人的用户界面,同时保持前端和后端代码的清晰分离。
静态文件夹结构:
static/
├── css/
│ └── style.css # 语音聊天界面的样式
│
├── js/
│ └── app.js # 客户端WebSocket处理和音频处理
│
└── assets/
└── audio/ # 音频相关资源(如果有)
关键组件:
JavaScript(app.js):
- WebSocket连接管理
- 音频录制和流传输
- 语音活动可视化
- 处理服务器响应(转录和AI响应)
CSS(style.css):
- 语音聊天界面样式
- 语音检测的视觉反馈
- 响应显示格式
在main.py中,静态文件是通过以下方式挂载的:
app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")这种设置使得实时语音聊天界面能够通过WebSocket连接顺畅运行,并为语音检测和响应提供视觉反馈。
代码逻辑实现
main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket, Request, WebSocketDisconnect
from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
import uvicorn
import json
import asyncio
import logging
import numpy as np
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import tempfile
import wave
from config import config
#
import webrtcvad
import numpy as np
import struct
import logging
#
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = config.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
os.environ["GROQ_API_KEY"] = config.get("GROQ_API_KEY")
#
#
## Audio Detection
######################################################################
class VoiceDetector:
def __init__(self, sample_rate=16000, frame_duration=30):
self.vad = webrtcvad.Vad(2) # Reduced aggressiveness for better continuous speech detection
self.sample_rate = sample_rate
self.frame_duration = frame_duration
self.frame_size = int(sample_rate * frame_duration / 1000)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
self.silence_frames = 0
self.max_silence_frames = 15 # Allow more silence between words
self.min_speech_frames = 3 # Require minimum speech frames to avoid spurious detections
self.speech_frames = 0
self.is_speaking = False
def _frame_generator(self, audio_data):
"""Generate audio frames from raw audio data."""
if len(audio_data) < self.frame_size:
self.logger.warning(f"Audio data too short: {len(audio_data)} bytes")
return []
n = len(audio_data)
offset = 0
frames = []
while offset + self.frame_size <= n:
frames.append(audio_data[offset:offset + self.frame_size])
offset += self.frame_size
return frames
def _convert_audio_data(self, audio_data):
"""Convert audio data to the correct format."""
try:
# First try to interpret as float32
float_array = np.frombuffer(audio_data, dtype=np.float32)
# Convert float32 [-1.0, 1.0] to int16 [-32768, 32767]
int16_array = (float_array * 32767).astype(np.int16)
return int16_array
except ValueError:
try:
# If that fails, try direct int16 interpretation
return np.frombuffer(audio_data, dtype=np.int16)
except ValueError as e:
# If both fail, try to pad the data to make it aligned
padding_size = (2 - (len(audio_data) % 2)) % 2
if padding_size > 0:
padded_data = audio_data + b'\x00' * padding_size
return np.frombuffer(padded_data, dtype=np.int16)
raise e
def detect_voice(self, audio_data):
"""
Detect voice activity in audio data.
Args:
audio_data (bytes): Raw audio data
Returns:
bool: True if voice activity is detected, False otherwise
"""
try:
if audio_data is None or len(audio_data) == 0:
self.logger.warning("Audio data is empty or None")
return False
# Convert audio data to the correct format
try:
audio_array = self._convert_audio_data(audio_data)
if len(audio_array) == 0:
self.logger.warning("No valid audio data after conversion")
return False
except ValueError as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error converting audio data: {str(e)}")
return False
# Process frames
frames = self._frame_generator(audio_array)
if not frames:
self.logger.warning("No frames generated from audio data")
return False
# Count speech frames in this chunk
current_speech_frames = 0
for frame in frames:
try:
# Pack the frame into bytes
frame_bytes = struct.pack("%dh" % len(frame), *frame)
# Check for voice activity
if self.vad.is_speech(frame_bytes, self.sample_rate):
current_speech_frames += 1
self.speech_frames += 1
self.silence_frames = 0
else:
self.silence_frames += 1
except struct.error as se:
self.logger.error(f"Error packing frame data: {str(se)}")
continue
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error processing frame: {str(e)}")
continue
# Update speaking state
if current_speech_frames > 0:
if not self.is_speaking and self.speech_frames >= self.min_speech_frames:
self.is_speaking = True
return True
elif self.silence_frames > self.max_silence_frames:
if self.is_speaking:
self.is_speaking = False
self.speech_frames = 0
return False
# Keep current state if in transition
return self.is_speaking
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error in voice detection: {str(e)}")
return False
# Set up logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Initialize OpenAI and Groq clients
openai_client = AsyncOpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
#
groq_client = AsyncOpenAI(
base_url="https://api.groq.com/openai/v1",
api_key=os.getenv("GROQ_API_KEY")
)
app = FastAPI()
# Mount static files
app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")
@app.get("/", response_class=HTMLResponse)
async def get_index(request: Request):
return templates.TemplateResponse("index.html", {"request": request})
async def transcribe_audio(audio_data: bytes):
"""Transcribe audio using Groq's Whisper model"""
temp_wav = None
try:
# Create a unique temporary file
temp_wav = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix='.wav', delete=False)
wav_path = temp_wav.name
temp_wav.close() # Close the file handle immediately
# Write the WAV file
with wave.open(wav_path, 'wb') as wav_file:
wav_file.setnchannels(1) # Mono
wav_file.setsampwidth(2) # 2 bytes per sample (16-bit)
wav_file.setframerate(16000) # 16kHz
wav_file.writeframes(audio_data)
# Transcribe using Groq
with open(wav_path, 'rb') as audio_file:
response = await groq_client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-large-v3-turbo",
file=audio_file,
response_format="text"
)
return response
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Transcription error: {str(e)}")
return None
finally:
# Clean up the temporary file
if temp_wav is not None:
try:
os.unlink(temp_wav.name)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error deleting temporary file: {str(e)}")
async def get_chat_response(text: str):
"""Get chat response from Groq"""
try:
response = await groq_client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama-3.1-70b-versatile",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please provide a clear, concise, and accurate response."},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
],
temperature=0,
max_tokens=500
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Chat response error: {str(e)}")
return None
async def generate_speech(text: str):
"""Generate speech using OpenAI TTS"""
try:
response = await openai_client.audio.speech.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy",
input=text
)
# Get the speech data directly from the response
# No need to await response.read() as the response is already the audio data
return response.content
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Speech generation error: {str(e)}")
return None
@app.websocket("/ws")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
await websocket.accept()
logger.info("WebSocket connection established")
voice_detector = VoiceDetector()
audio_buffer = bytearray()
silence_duration = 0
max_silence_duration = 1.5 # seconds
frames_per_second = 1000 / voice_detector.frame_duration # frames per second
max_silence_frames = int(max_silence_duration * frames_per_second)
try:
while True:
try:
data = await websocket.receive_bytes()
if not data:
logger.warning("Received empty data frame")
continue
# Check for voice activity
voice_detected = voice_detector.detect_voice(data)
if voice_detected:
# Reset silence counter and add to buffer
silence_duration = 0
audio_buffer.extend(data)
await websocket.send_json({"type": "vad", "status": "active"})
else:
# Increment silence counter
silence_duration += 1
# If we were collecting speech and hit max silence, process the buffer
if len(audio_buffer) > 0 and silence_duration >= max_silence_frames:
logger.info(f"Processing audio buffer of size: {len(audio_buffer)} bytes")
# Process the complete utterance
transcription = await transcribe_audio(bytes(audio_buffer))
if transcription:
logger.info(f"Transcription: {transcription}")
await websocket.send_json({
"type": "transcription",
"text": transcription
})
# Get chat response
chat_response = await get_chat_response(transcription)
if chat_response:
logger.info(f"Chat response: {chat_response}")
await websocket.send_json({
"type": "chat_response",
"text": chat_response
})
# Generate and send voice response
voice_response = await generate_speech(chat_response)
if voice_response:
logger.info("Generated voice response")
await websocket.send_bytes(voice_response)
# Clear the buffer after processing
audio_buffer = bytearray()
await websocket.send_json({"type": "vad", "status": "inactive"})
elif len(audio_buffer) > 0:
# Still collecting silence, add to buffer
audio_buffer.extend(data)
except WebSocketDisconnect:
logger.info("WebSocket disconnected")
break
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error processing websocket frame: {str(e)}")
continue
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"WebSocket connection error: {str(e)}")
finally:
logger.info("Closing WebSocket connection")
await websocket.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("main:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, reload=True)
启动应用程序
python main.py
INFO: Will watch for changes in these directories: ['D:\\Voice_detection_and_response']
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
INFO: Started reloader process [32716] using StatReload
INFO: Started server process [33080]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: 127.0.0.1:57903 - "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 OK
INFO: 127.0.0.1:57903 - "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 Not Found
语音助手应用
INFO: ('127.0.0.1', 56153) - "WebSocket /ws" [accepted]
INFO:main:WebSocket connection established
INFO: connection open
INFO:main:Processing audio buffer of size: 165888 bytes
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/audio/transcriptions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
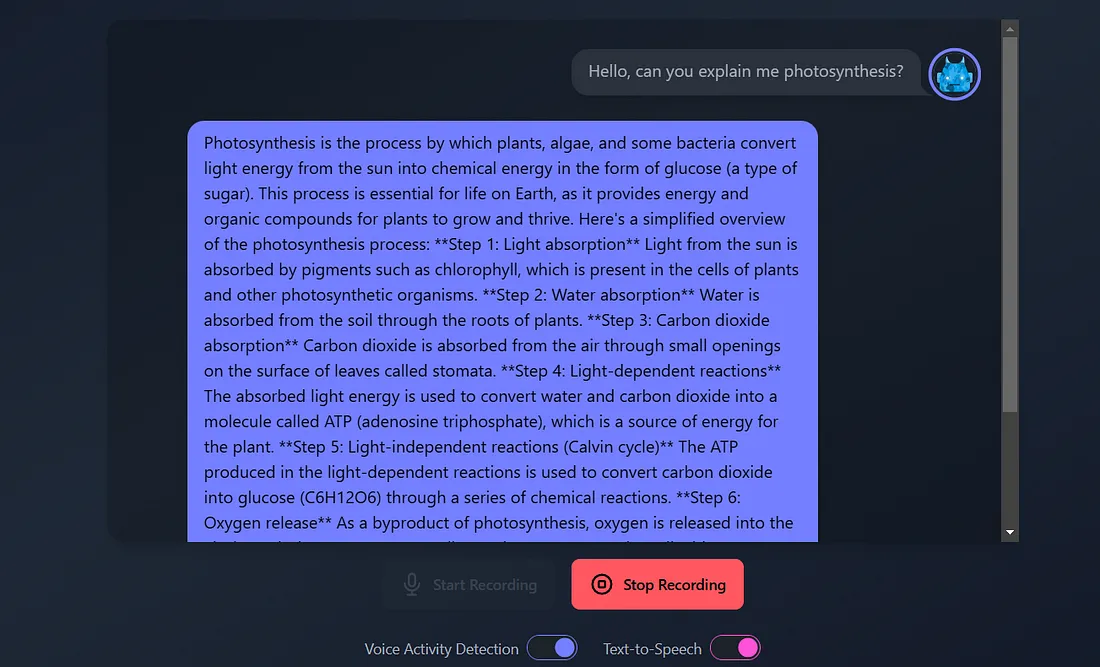
INFO:main:Transcription: Hello, can you explain me photosynthesis?
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Chat response: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (a type of sugar). This process is essential for life on Earth, as it provides energy and organic compounds for plants to grow and thrive.
Here's a simplified overview of the photosynthesis process:
**Step 1: Light absorption**
Light from the sun is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll, which is present in the cells of plants and other photosynthetic organisms.
**Step 2: Water absorption**
Water is absorbed from the soil through the roots of plants.
**Step 3: Carbon dioxide absorption**
Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air through small openings on the surface of leaves called stomata.
**Step 4: Light-dependent reactions**
The absorbed light energy is used to convert water and carbon dioxide into a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is a source of energy for the plant.
**Step 5: Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle)**
The ATP produced in the light-dependent reactions is used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose (C6H12O6) through a series of chemical reactions.
**Step 6: Oxygen release**
As a byproduct of photosynthesis, oxygen is released into the air through the stomata.
**Overall equation:**
6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen)
In summary, photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, releasing oxygen as a byproduct and producing glucose, which is used to fuel their growth and development.
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/audio/speech "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Generated voice response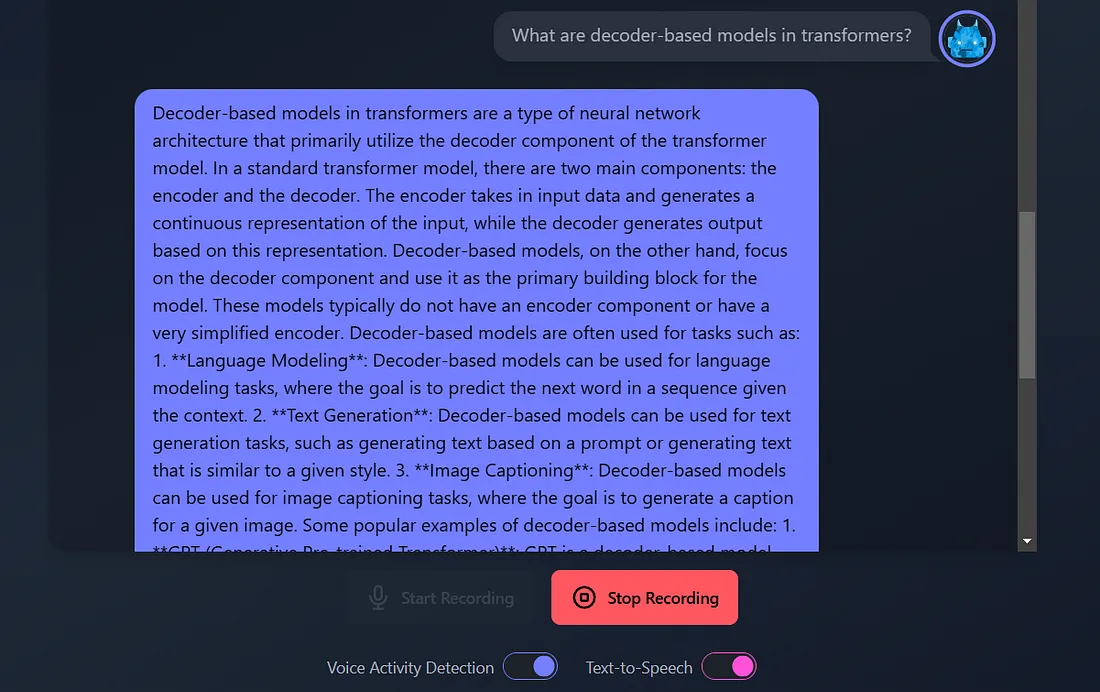
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Chat response: Decoder-based models in transformers are a type of neural network architecture that primarily relies on the decoder component of the transformer model. Here's a concise overview:
**What is a Transformer?**
A transformer is a type of neural network architecture introduced in the paper "Attention is All You Need" by Vaswani et al. in 2017. It's primarily used for sequence-to-sequence tasks, such as machine translation, text summarization, and text generation.
**Decoder Component**
In a transformer model, the decoder component is responsible for generating the output sequence, one token at a time. The decoder takes the output of the encoder component and uses it to generate the next token in the sequence.
**Decoder-Based Models**
Decoder-based models are a type of transformer model that focuses primarily on the decoder component. These models use the decoder to generate text, without the need for an encoder component. The input to the decoder is typically a sequence of tokens, such as a prompt or a prefix, and the output is a generated sequence of tokens.
**Key Characteristics**
Decoder-based models have the following key characteristics:
1. **Autoregressive**: Decoder-based models are autoregressive, meaning that they generate text one token at a time, based on the previous tokens in the sequence.
2. **No Encoder**: Decoder-based models do not have an encoder component, which means they do not have a separate component for encoding the input sequence.
3. **Self-Attention**: Decoder-based models use self-attention mechanisms to attend to different parts of the input sequence and generate the next token.
**Examples of Decoder-Based Models**
Some examples of decoder-based models include:
1. **Language Models**: Language models, such as BERT and RoBERTa, use a decoder-based architecture to generate text.
2. **Text Generation Models**: Text generation models, such as transformer-XL and XLNet, use a decoder-based architecture to generate text.
3. **Chatbots**: Chatbots, such as those built using the transformer-XL architecture, use a decoder-based architecture to generate responses to user input.
**Advantages**
Decoder-based models have several advantages, including:
1. **Flexibility**: Decoder-based models can be fine-tuned for a variety of tasks, such as text generation, language translation, and text summarization.
2. **Efficiency**: Decoder-based models can be more efficient than encoder-decoder models, since they do not require a separate encoder component.
3. **Improved
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/audio/speech "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Generated voice response
INFO:main:Processing audio buffer of size: 143360 bytes
INFO: 127.0.0.1:57312 - "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 Not Found
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/audio/transcriptions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Transcription: E aí
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.groq.com/openai/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Chat response: Tudo bem! Como posso ajudar você hoje?
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/audio/speech "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
INFO:main:Generated voice response
结论
本项目展示了将现代Web框架与AI服务相结合,创建复杂语音应用的强大能力。该架构为构建可扩展的实时语音处理系统提供了坚实的基础。
FastAPI的高性能、WebSocket的实时功能以及最先进的AI服务的结合,为基于语音的交互创建了一个强大的平台。这一架构可扩展应用于各种领域,从虚拟助手到辅助工具等。































