基于Llama.cpp和LLaVA的全开源RAG实现
检索增强生成(RAG)系统是从非结构化数据中提取见解的强大工具。随着开源技术的进步,现在有可能构建一个完全开源的RAG系统,该系统能够同时处理文本和图像。在本文中,我们将逐步介绍构建此类系统时所做的设计选择和所使用的工具。我们将使用Llama作为大型语言模型(你可以使用Llama.cpp,也可以使用Transformers库中的Llama进行语言处理,并使用LLaVA进行视觉数据集成)。
系统概述
我们的RAG系统处理文本和视觉数据,以准确回答查询并提供可操作的见解。以下是系统架构的高级概述:
- 文本检索和生成:使用Llama.cpp进行高效的本地文本处理。
- 视觉集成:使用LLaVA总结图像(图表、图形等)。
- 嵌入和检索:通过Pgvector存储和检索文档嵌入。(Qdrant和ChromaDB也是不错的选择)
- 管道编排:使用llama-index管理检索和响应生成。(你也可以使用Langchain)
这是架构的示意图:
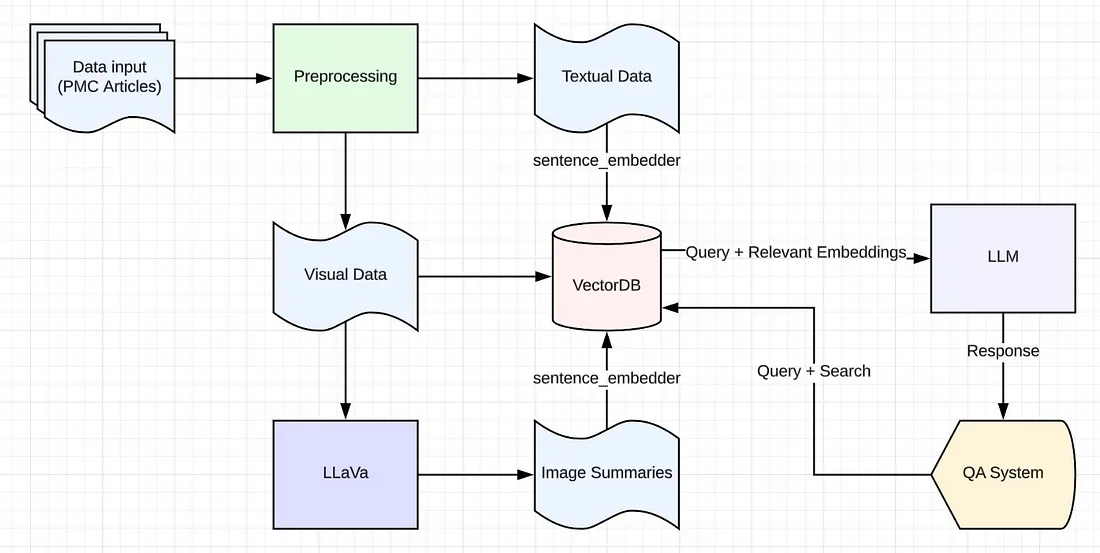
关键设计选择
PDF预处理
一个稳健的预处理流程对于确保向RAG系统提供高质量的输入至关重要。原始数据中的格式不一致、不必要的伪影和破损的结构可能会显著降低模型性能。
第一部分是文本预处理:
from llama_index.readers.file import PyMuPDFReader
import re
from llama_index.readers.file import PyMuPDFReader
import fitz # PyMuPDF for image extraction
# Define stop keywords
# My keywords are as follows because of my data domain: Academic papers
stop_keywords = ["References", "Conflict of interest",
"Acknowledgements", "Supplementary Materials", "Author details", "Publishers Note"]
# Regex to capture figures
figure_pattern = r'\b(Figure|Fig\.)\s*\d+[a-zA-Z]*\b.*?(\n.*?)*?(?=\n\n|\Z)'
def preprocess_text(text, stop_keywords):
"""Preprocess text by stopping at the earliest occurrence of any keyword, ignoring case."""
earliest_position = len(text) # Default to the end of the text
for keyword in stop_keywords:
pattern = rf"\b{re.escape(keyword)}\b" # Match exact word boundaries
match = re.search(pattern, text, re.IGNORECASE)
if match:
earliest_position = min(earliest_position, match.start())
return text[:earliest_position]
def clean_text(block_text):
"""Clean and process individual blocks of text."""
block_text = " ".join(block_text.split()) # Remove extra spaces and newlines
block_text = re.sub(r'^\d+\.\s+', '', block_text) # Remove section numbering
block_text = re.sub(r'[^A-Za-z0-9\s,.]', '', block_text) # Keep only basic punctuation and letters
if len(block_text) < 10 or re.match(r'Page \d+', block_text):
return None # Skip short blocks or page numbers
if re.search(r'\d{2,}', block_text) and re.search(r'(\d+\.\d+|\d+%)', block_text):
return None # Skip blocks with many numeric values
if re.search(r'\b(Table|Effect|Mediation|Summary|IV|Mediator|Cont)\b', block_text, re.IGNORECASE):
return None
return block_text
我们还需要从PDF中提取图像并将其保存以供后续处理:
def extract_figures(text):
"""Extract figure captions or descriptions from the text."""
figures = re.findall(figure_pattern, text, re.IGNORECASE | re.DOTALL)
return [" ".join(fig).strip() for fig in figures if len(" ".join(fig).strip()) > 5] # Filter out short/no-content matches
def extract_images_from_pdf(pdf_path, output_dir, pdf_name):
"""Extract images from a PDF and save them to output_dir."""
document = fitz.open(pdf_path)
for page_idx in range(len(document)):
page = document.load_page(page_idx)
images = page.get_images(full=True)
for img_index, img in enumerate(images):
xref = img[0]
base_image = document.extract_image(xref)
image_bytes = base_image["image"]
image_ext = base_image["ext"]
# Save the image
image_filename = output_dir / f"{pdf_name}_page{page_idx}_img{img_index}.{image_ext}"
with image_filename.open("wb") as img_file:
img_file.write(image_bytes)
print(f"Saved image: {image_filename}")
document.close()
语言模型:Llama.cpp
为何选择Llama.cpp?
- 针对本地部署进行了优化,资源需求极低。
- 支持高效量化,使得像Llama-2–13B-chat这样的模型能够在普通硬件上运行。
- 不依赖于GPU,降低了设置复杂度。
实施提示:
- 使用预先量化的GGML模型,以避免繁琐的量化步骤。
- 为检索增强任务微调提示,以确保获得相关且简洁的答案。
from llama_index.llms.llama_cpp import LlamaCPP
#from langchain_community.llms import LlamaCpp (alternative)
model_path = "your_path_here/llama-2-13b-chat.Q4_0.gguf"
# Extra parameters
# n_gpu_layers = -1 # The number of layers to put on the GPU. The rest will be on the CPU. If you don't know how many layers there are, you can use -1 to move all to GPU.
# n_batch = 512 # Should be between 1 and n_ctx, consider the amount of VRAM in your GPU.
llm = LlamaCPP(
model_path=model_path,
temperature=0.1,
max_new_tokens=256,
context_window=4000,
generate_kwargs={},
model_kwargs={"n_gpu_layers": 1},
#f16_kv=True, # For M2: MUST set to True, otherwise you will run into problem after a couple of calls
#callback_manager=callback_manager, # Need to call with langchain
verbose=True,
)
视觉总结:LLaVA
为何要为图像生成文本总结?
- 许多数据集中的视觉内容较为稀疏,导致多模态嵌入的效果不佳。
- 将图表和示意图转换为文本可以确保与基于文本的流水线兼容。
- 如果你打算使用像CLIP或ALIGN这样的模型,可能会丢失大量文本信息。
如何使用LLaVA:
- 使用像PyMuPDF或Pillow这样的库从文档中提取视觉元素。
- 将图像通过LLaVA处理以生成文本总结。
- 使用sentence-transformers将这些总结与文档文本一起嵌入。
from transformers import AutoProcessor, LlavaForConditionalGeneration
# Load LLaVA processor and model
model_name = "llava-hf/llava-1.5-7b-hf"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = LlavaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
# Create summaries for images
# Prompt can become more specific
# Example: Add context from the latest text chunk
image = Image.open(image_file).convert("RGB")
# Define the conversation template for generating a detailed description
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image"}, # Image placeholder
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"}
],
}
]
# Apply chat template and prepare inputs
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = processor(text=[text_prompt], images=[image], return_tensors="pt").to(device) # Ensure inputs are on the same device
# Generate response
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=256)
summary = processor.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
# Extract only the assistant's response
assistant_reply = summary.split("ASSISTANT:")[1].strip() if "ASSISTANT:" in summary else summary
image_summaries[image_file.name] = assistant_reply
print(f"Generated summary for {image_file.name}:\n{assistant_reply}\n")
嵌入和检索:Pgvector
为何选择Pgvector?
- 与PostgreSQL无缝集成,实现可扩展的向量存储。
- 支持使用嵌入进行高效的相似性搜索。
设置提示:
- 使用sentence-transformers(例如BAAI/bge-small-en)进行轻量级且有效的文本嵌入。我们也可以使用其他模型,集成很容易。
- 对于动态数据集,定期为新的嵌入建立索引。
# DB Connection:
db_name = "rag_db" # Use the database name
host = "localhost"
password = "password"
port = "5432" # Default PostgreSQL port
user = "myuser"
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname=db_name,
host=host,
password=password,
port=port,
user=user,
)
conn.autocommit = True
在代码的数据库部分添加检查是有意义的,因为我们不需要反复将相同的嵌入添加到同一个表中。以下是一个如何实现这一点的示例:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
from sqlalchemy.exc import OperationalError
from llama_index.vector_stores.postgres import PGVectorStore
# Connection parameters
db_params = {
"user": "myuser",
"password": "password",
"host": "localhost",
"port": "5432",
"database": "rag_db"
}
# Create SQLAlchemy engine
engine = create_engine(f"postgresql://{db_params['user']}:{db_params['password']}@{db_params['host']}:{db_params['port']}/{db_params['database']}")
# Update table name to include 'data_' prefix
table_name = "data_pmc_table" # Postgre adds 'data' in front of table_name
embed_dim = 384 # Embedding dimension
try:
with engine.connect() as conn:
# Check if the table exists
result = conn.execute(text(f"""
SELECT EXISTS (
SELECT FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'public' AND table_name = :table_name
);
"""), {"table_name": table_name}).scalar()
if result:
print(f"Table '{table_name}' exists. Cleaning it...")
conn.execute(text(f"DROP TABLE {table_name} CASCADE;"))
else:
print(f"Table '{table_name}' does not exist. Creating it...")
# Create a new table for vector store
vector_store = PGVectorStore.from_params(
database=db_params["database"],
host=db_params["host"],
password=db_params["password"],
port=db_params["port"],
user=db_params["user"],
table_name="pmc_table", # Use unprefixed name; PGVectorStore adds 'data_' automatically
embed_dim=embed_dim,
)
print(f"Table '{table_name}' has been created.")
except OperationalError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
print("Make sure the database exists and connection parameters are correct.")
协调:llama-index
为何选择llama-index?
- 简化了复杂文档结构的检索流水线。
- 支持多模态扩展,能够整合文本和图像总结。
设计说明:
- 如果需要高级的代理功能,可以考虑切换到LangChain并使用LangGraph。虽然也可以使用llama-index来实现代理式检索增强生成(RAG),但我发现LangGraph更容易理解。
评估
评估对于衡量系统的准确性、连贯性和整体实用性至关重要。我们可以结合自动化的指标和针对文本及视觉组件定制的人工评估来进行。
我们还可以使用DeepEval进行基于大型语言模型(LLM)的评估。默认情况下,它使用GPT模型。
结论
构建一个完全开源的检索增强生成(RAG)系统是一项激动人心的挑战,具有巨大的价值。通过结合Llama.cpp、LLaVA和其他开源工具,我们创建了一个多功能流水线,填补了文本和视觉数据之间的鸿沟。































