Llama 3.2-Vision:多模态LLM的图像聊天功能
介绍
大型语言模型(LLM)与视觉能力的结合,正在通过多模态LLM(MLLM)引领计算机视觉领域的革命。这些模型结合了文本和视觉输入,在图像理解和推理方面展现出了令人印象深刻的能力。虽然这些模型以前只能通过API访问,但最近的开源选项已经允许本地执行,使它们在生产环境中更具吸引力。
在本文中,我们将学习如何使用开源的Llama 3.2-Vision模型与我们的图像进行“对话”,你将会对其OCR(光学字符识别)、图像理解和推理能力感到惊讶。
Llama 3.2-Vision背景介绍
Llama,即“Large Language Model Meta AI”的缩写,是Meta开发的一系列先进LLM。他们最新的Llama 3.2版本引入了先进的视觉能力。视觉变体有两种尺寸:110亿和900亿参数,支持在边缘设备上进行推理。Llama 3.2具有高达128k个标记的上下文窗口,并支持高达1120x1120像素的高分辨率图像,能够处理复杂的视觉和文本信息。
架构
Llama系列模型是仅解码器的Transformer模型。Llama 3.2-Vision是在预训练的Llama 3.1仅文本模型的基础上构建的。它采用标准的、密集的自回归Transformer架构,与其前身Llama和Llama 2相比没有显著偏离。
为了支持视觉任务,Llama 3.2使用预训练的视觉编码器(ViT-H/14)提取图像表示向量,并通过视觉适配器将这些表示集成到冻结的语言模型中。适配器由一系列交叉注意力层组成,使模型能够专注于与正在处理的文本相对应的图像特定部分。
适配器是在文本-图像对上进行训练的,以使图像表示与语言表示对齐。在适配器训练期间,图像编码器的参数会得到更新,而语言模型的参数则保持冻结状态,以保留现有的语言能力。
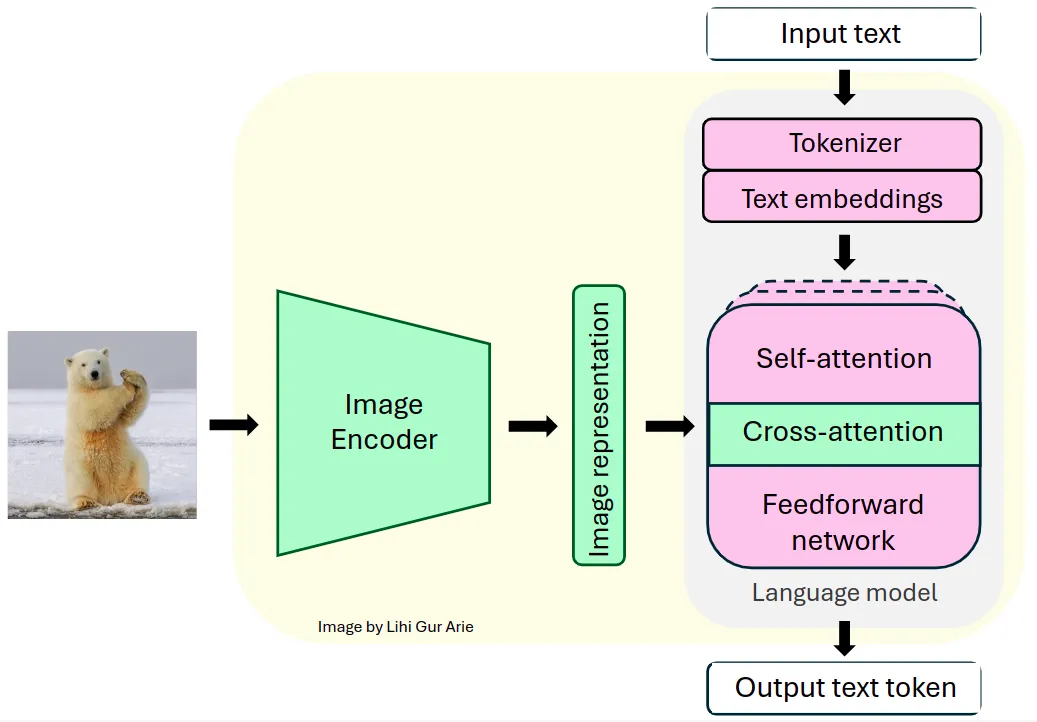
这种设计使Llama 3.2在多模态任务中表现出色,同时保持了其强大的仅文本处理能力。由此产生的模型在需要图像和语言理解的任务中展现出了令人印象深刻的能力,并允许用户与他们的视觉输入进行交互式通信。
实践
在了解了Llama 3.2的架构之后,我们可以深入实践实现部分。
加载模型
我们设置好了环境并获得了必要的权限,我们将使用Hugging Face的Transformers库来实例化模型及其关联的处理器。处理器负责为模型准备输入并格式化其输出。
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct"
model = MllamaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
预期聊天模板
聊天模板通过存储“用户”(us)和“助手”(AI模型)之间的交流来维护对话历史。对话历史被构造成一个名为messages的字典列表,其中每个字典代表一个单一的对话回合,包括用户和模型的响应。用户的回合可以包含图像-文本或仅文本输入,其中{"type": "image"}表示图像输入。
例如,在几次聊天迭代之后,messages列表可能看起来像这样:
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "image"}, {"type": "text", "text": prompt1}]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": generated_texts1}]},
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt2}]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": generated_texts2}]},
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt3}]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": generated_texts3}]}
]
这个messages列表之后会被传递给apply_chat_template()方法,以将对话转换成模型期望格式的单个可标记字符串。
主要功能
在本文中,我提供了一个chat_with_mllm函数,该函数能够实现与Llama 3.2 MLLM的动态对话。此函数负责加载图像、预处理图像和文本输入、生成模型响应,并管理对话历史以支持聊天模式交互。
def chat_with_mllm (model, processor, prompt, images_path=[],do_sample=False, temperature=0.1, show_image=False, max_new_tokens=512, messages=[], images=[]):
# Ensure list:
if not isinstance(images_path, list):
images_path = [images_path]
# Load images
if len (images)==0 and len (images_path)>0:
for image_path in tqdm (images_path):
image = load_image(image_path)
images.append (image)
if show_image:
display ( image )
# If starting a new conversation about an image
if len (messages)==0:
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "image"}, {"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
# If continuing conversation on the image
else:
messages.append ({"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]})
# process input data
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True)
inputs = processor(images=images, text=text, return_tensors="pt", ).to(model.device)
# Generate response
generation_args = {"max_new_tokens": max_new_tokens, "do_sample": True}
if do_sample:
generation_args["temperature"] = temperature
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs,**generation_args)
generate_ids = generate_ids[:, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:-1]
generated_texts = processor.decode(generate_ids[0], clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)
# Append the model's response to the conversation history
messages.append ({"role": "assistant", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": generated_texts}]})
return generated_texts, messages, images
与Llama聊天
蝴蝶图片示例
在我们的第一个示例中,我们将与Llama 3.2就一张蝴蝶孵化的图片进行聊天。由于Llama 3.2-Vision在使用图片时不支持系统提示,我们将直接把指令添加到用户提示中,以引导模型的响应。通过设置do_sample=True和temperature=0.2,我们可以在保持响应连贯性的同时,引入轻微的随机性。如果你想要固定的答案,可以设置do_sample=False。messages参数用于保存聊天历史,最初是空的,就像images参数一样。
instructions = "Respond concisely in one sentence."
prompt = instructions + "Describe the image."
response, messages,images= chat_with_mllm ( model, processor, prompt,
images_path=[img_path],
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.2,
show_image=True,
messages=[],
images=[])
# Output: "The image depicts a butterfly emerging from its chrysalis,
# with a row of chrysalises hanging from a branch above it."
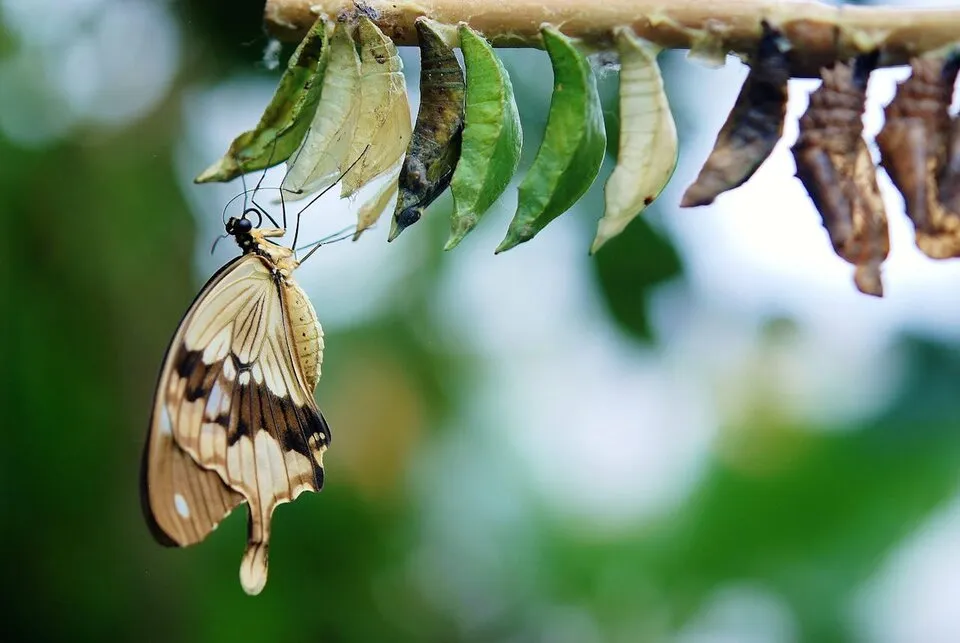

如我们所见,输出准确且简洁,表明模型有效地理解了图像。
在下一次聊天迭代中,我们将传递一个新的提示,以及聊天历史(messages)和图像文件(images)。这个新的提示旨在评估Llama 3.2的推理能力:
prompt = instructions + "What would happen to the chrysalis in the near future?"
response, messages, images= chat_with_mllm ( model, processor, prompt,
images_path=[img_path,],
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.2,
show_image=False,
messages=messages,
images=images)
# Output: "The chrysalis will eventually hatch into a butterfly."
我们在提供的Colab笔记本中继续了这次聊天,并获得了以下对话:

这次对话通过准确描述场景,突出了模型理解图像的能力。它还通过逻辑连接信息,正确地推断出蛹将会发生什么,并解释了为什么有些是棕色的而有些是绿色的,从而展示了其推理能力。
表情包图像示例
在这个示例中,我将向模型展示我自己创建的一个表情包,以评估Llama的OCR(光学字符识别)能力,并确定它是否能理解我的幽默感。
instructions = "You are a computer vision engineer with sense of humor."
prompt = instructions + "Can you explain this meme to me?"
response, messages,images= chat_with_mllm ( model, processor, prompt,
images_path=[img_path,],
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.5,
show_image=True,
messages=[],
images=[])
这是输入的表情包:
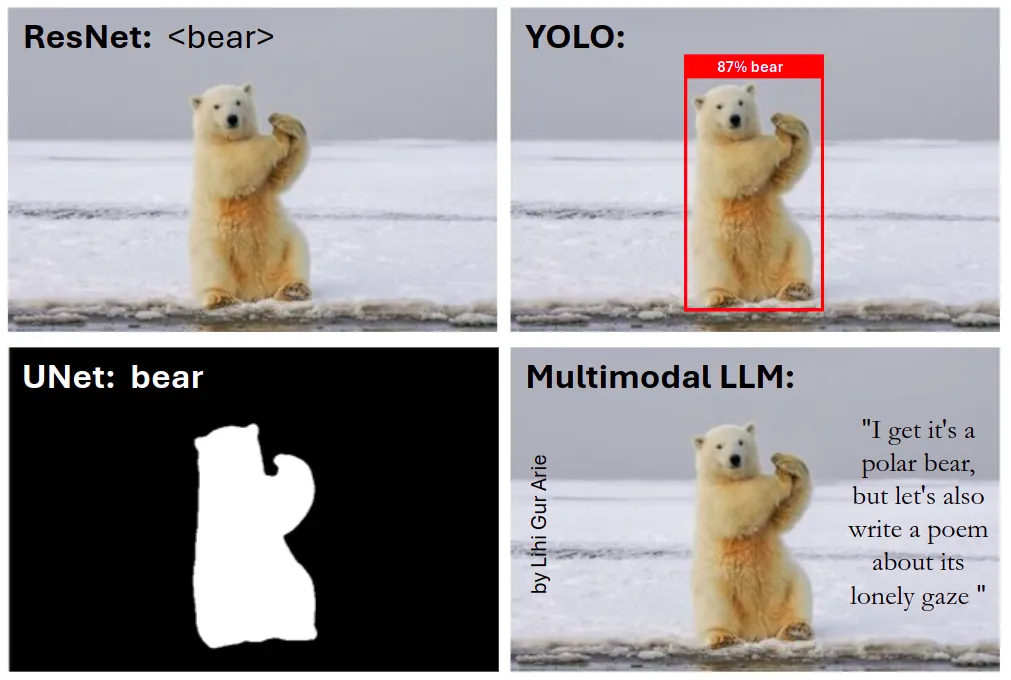
这是模型的回应:

如我们所见,模型展现出了出色的OCR能力,并且理解了图像中文本的含义。
总结
在本文中,我们学习了如何在本地构建Llama 3.2-Vision模型,并管理聊天式的交互历史,从而增强用户参与度。我们探索了Llama 3.2的零样本能力,并对其场景理解、推理和OCR技能印象深刻。































