LangGraph和Whisper实战:重建ElevenLabs AI代理全流程
在亲身体验了ElevenLabs的AI代理功能,并发现无需编写大量代码就能快速构建一个功能齐全的语音机器人后,我不禁思考——如果我从头开始构建会怎样?
使用LangGraph、ElevenLabs的API和Whisper从头开始重建AI语音机器人。我的目标是更深入地了解其内部工作原理,优化其性能,并探索现成解决方案无法提供的新可能性。在本文中,我不仅将带你深入了解我如何构建自己版本的ElevenLabs AI代理,还将为你提供一个清晰的框架,让你自己也能重建一个语音机器人。在此过程中,我将分享我所面临的挑战、我所做的决策,以及定制编码解决方案的灵活性如何解锁无限可能。
AI语音机器人的构建模块
为了将这个项目变为现实,我依赖了三个基本组件,它们构成了AI语音机器人的基础:
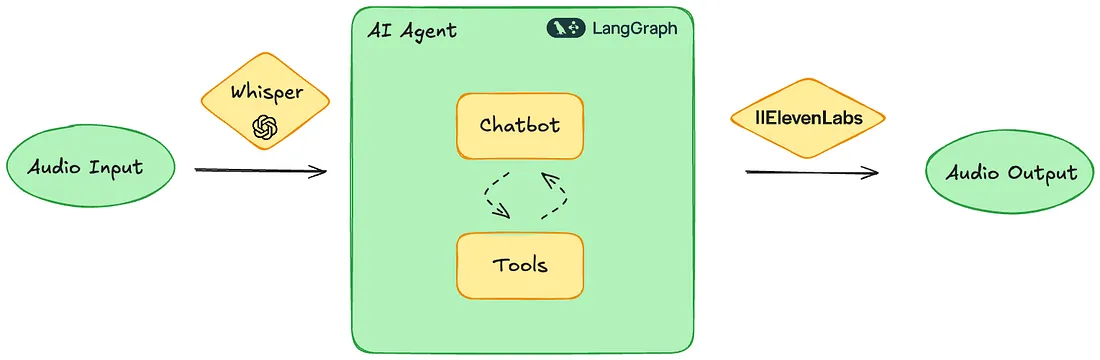
语音转文字:Whisper
Whisper是由OpenAI开发的一种先进的语音转文字模型,以其准确性和多语言能力而闻名。它能够高效地将口语转换成文字,是处理高精度语音输入的理想解决方案。其深度学习能力使其能够理解各种口音和方言,确保在不同人群中都能提供流畅的用户体验。在这个项目中,我使用了OpenAI的Python SDK来处理音频输入:
openai_client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1",
file=audio_bytes,
)
对话式AI代理:LangGraph
LangGraph由LangChain开发,作为AI语音机器人的大脑,支持创建结构化、交互式的对话,具备工具调用和记忆功能。它能够管理复杂的对话流程和决策过程,确保机器人能够对广泛的用户输入做出智能响应。通过LangGraph,我设计了一种高度动态且适应性强的对话体验,能够记住之前的交互,并高效地利用各种工具来增强功能。
文本转语音:ElevenLabs API
ElevenLabs API为文本转语音组件提供支持,提供自然且逼真的语音响应。该组件通过输出类似人类的语音,增强了用户交互,使对话更加引人入胜且直观。在这个项目中,我使用ElevenLabs的Python SDK,通过eleven_turbo_v2_5模型从文本生成语音:
elevenlabs_client.text_to_speech.convert(
voice_id="YUdpWWny7k5yb4QCeweX",
output_format="mp3_22050_32",
text=cleaned_text,
model_id="eleven_turbo_v2_5",
voice_settings=VoiceSettings(
stability=0.0,
similarity_boost=1.0,
style=0.0,
use_speaker_boost=True,
),
)
这些组件共同使我能够从零开始创建一个高度响应且智能的语音机器人。
逐步构建AI语音机器人
既然我们已经介绍了基本的构建模块,那么让我们深入实现过程。我们将首先使用LangGraph创建一个具备记忆功能和获取当前日期时间工具的基本对话式聊天机器人。一旦聊天机器人开始运行,我们将通过添加两个额外节点来增强其功能——一个用于使用Whisper将传入的音频转换为文本,另一个用于使用ElevenLabs API将聊天机器人的响应转换为音频。这种逐步的方法将提供一个坚实的基础,同时逐步构建语音机器人的能力。
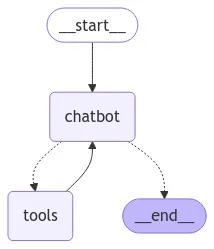
第一步:构建基本对话式聊天机器人
首先,我们将创建一个简单的聊天机器人,它能够记住之前的消息并获取当前日期时间。这将涉及定义一个状态管理系统,集成一个从API获取日期和时间的工具,并使用LangGraph构建对话流程。
定义状态管理系统
我们首先定义聊天机器人的状态,以便跟踪对话消息。
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
State类使用一个带注释的列表来存储消息,并在收到新消息时将其追加到列表中。
实现记忆功能
接下来,我们引入记忆功能来存储和检索之前的消息,确保对话的连续性。
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
MemorySaver组件有助于在交互过程中持久保存聊天机器人的状态。
定义工具
接下来,我们定义一个工具来从API获取当前日期和时间。
from langchain_core.tools import tool
import requests
@tool
def get_date_and_time() -> dict:
"""
Call tool to fetch the current date and time from an API.
"""
try:
response = requests.get("https://timeapi.io/api/Time/current/zone?timeZone=Europe/Brussels")
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
return {"date_time": data["dateTime"], "timezone": data["timeZone"]}
except requests.RequestException as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
这个函数获取当前日期和时间,并以JSON格式返回。
设置语言模型
现在,我们设置语言模型并将其与定义的工具集成,使聊天机器人能够在其响应中调用外部工具。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([get_date_and_time])
构建对话流程
使用LangGraph,我们现在构建一个简单的对话流程,该流程仅依赖一个可以访问get_date_and_time工具的“聊天机器人”节点。
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
def chatbot(state: State, config: RunnableConfig):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
# initiate the graph
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
graph_builder.add_edge("chatbot", "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
这种设置使聊天机器人能够处理消息、将其存储在内存中并相应地做出响应。
第二步:为聊天机器人增加语音功能
接下来,我们将在聊天机器人工作流程中添加两个额外节点——一个用于使用Whisper将传入的音频转换为文本,另一个用于使用ElevenLabs API将文本响应转换为音频。这一增强功能将使聊天机器人转变为一个功能齐全的语音助手。
输入:捕获音频
为了实现无缝且互动的体验,聊天机器人必须能够准确地倾听并理解用户。这就是OpenAI的Whisper模型发挥作用的地方,它使聊天机器人能够有效地捕获并转录口语。
语音转文本过程包括几个关键步骤:
音频捕获:使用sounddevice库,聊天机器人监听用户麦克风的声音输入。当检测到声音时,录音过程自动开始,并在一段沉默后停止。
处理音频输入:配置了多个参数以优化语音检测:
- SAMPLE_RATE:定义采样率,以确保充分捕获声音。
- THRESHOLD:设置检测语音活动的最小音频级别。
- SILENCE_DURATION:确定在停止录音前应保持多长时间的沉默。
- CHUNK_SIZE:指定处理音频块的大小。
语音识别:一旦录制了音频,就使用OpenAI的Whisper API进行处理并转录为文本,该API支持高精度的多语言语音识别。
import io
import threading
import numpy as np
import sounddevice as sd
from scipy.io.wavfile import write
from openai import OpenAI
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState, HumanMessage
# Initialize OpenAI client
openai_client = OpenAI()
# Audio settings
SAMPLE_RATE = 16000 # Adequate for human voice frequency
THRESHOLD = 500 # Silence detection threshold (adjust if needed)
SILENCE_DURATION = 1.5 # Duration (seconds) of silence before stopping
CHUNK_SIZE = 1024 # Number of frames per audio chunk
def record_audio_until_silence(state: MessagesState):
"""Waits for the user to start speaking, records the audio, and stops after detecting silence."""
audio_data = [] # List to store audio chunks
silent_chunks = 0 # Counter for silent chunks
started_recording = False # Flag to track if recording has started
def record_audio():
"""Continuously records audio, waiting for the user to start speaking."""
nonlocal silent_chunks, audio_data, started_recording
with sd.InputStream(samplerate=SAMPLE_RATE, channels=1, dtype='int16') as stream:
print("Waiting for you to start speaking...")
# Keep waiting indefinitely for the user to start talking
while not started_recording:
audio_chunk, _ = stream.read(CHUNK_SIZE)
audio_array = np.frombuffer(audio_chunk, dtype=np.int16)
# Check if there is voice input
if np.abs(audio_array).max() > THRESHOLD:
started_recording = True
print("Voice detected. Recording started.")
audio_data.append(audio_chunk)
break
# Start recording once voice is detected
while True:
audio_chunk, _ = stream.read(CHUNK_SIZE)
audio_data.append(audio_chunk)
audio_array = np.frombuffer(audio_chunk, dtype=np.int16)
# Detect silence after user has finished speaking
if np.abs(audio_array).max() < THRESHOLD:
silent_chunks += 1
else:
silent_chunks = 0 # Reset if sound is detected
# Stop if silence is detected for the specified duration
if silent_chunks > (SILENCE_DURATION * SAMPLE_RATE / CHUNK_SIZE):
print("Silence detected. Stopping recording.")
break
# Start recording in a separate thread
recording_thread = threading.Thread(target=record_audio)
recording_thread.start()
recording_thread.join()
# Stack all audio chunks into a single NumPy array and write to file
audio_data = np.concatenate(audio_data, axis=0)
# Convert to WAV format in-memory
audio_bytes = io.BytesIO()
write(audio_bytes, SAMPLE_RATE, audio_data) # Use scipy's write function to save to BytesIO
audio_bytes.seek(0) # Go to the start of the BytesIO buffer
audio_bytes.name = "audio.wav" # Set a filename for the in-memory file
# Transcribe via Whisper
transcription = openai_client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1",
file=audio_bytes,
language='nl'
)
# Print the transcription
print("Here is the transcription:", transcription.text)
# Write to messages
return {"messages": [HumanMessage(content=transcription.text)]}
输出:通过语音让聊天机器人栩栩如生
为了提供真正引人入胜的用户体验,聊天机器人需要以自然且类似人类的方式进行交流。这就是ElevenLabs强大的文本转语音(TTS)功能发挥作用的地方,它使我们能够无缝地将聊天机器人的响应转换为逼真的音频。
该过程涉及几个关键步骤:
- 初始化ElevenLabs客户端:使用API密钥设置ElevenLabs API客户端,以启用与文本转语音服务的通信。
- 处理聊天机器人响应:在将文本转换为语音之前,会对聊天机器人的响应进行清理,以去除任何可能干扰音频输出的格式化工件。
- 将文本转换为语音:将清理后的文本发送到ElevenLabs API,利用高级语音设置来控制稳定性、相似度提升和说话者风格等方面。
- 播放生成的音频:一旦TTS转换完成,就将音频响应播放给用户,确保对话流畅自然。
以下是文本转语音转换的实现方式:
import os
from elevenlabs import play, VoiceSettings
from elevenlabs.client import ElevenLabs
from langgraph.graph import MessagesState
# Initialize ElevenLabs client
elevenlabs_client = ElevenLabs(api_key=os.getenv("ELEVEN_API_KEY"))
def play_audio(state: MessagesState):
"""Plays the audio response from the remote graph with ElevenLabs."""
# Response from the agent
response = state['messages'][-1]
# Prepare text by replacing ** with empty strings
cleaned_text = response.content.replace("**", "")
# Call text_to_speech API with turbo model for low latency
response = elevenlabs_client.text_to_speech.convert(
voice_id="YUdpWWny7k5yb4QCeweX", # Adam pre-made voice
output_format="mp3_22050_32",
text=cleaned_text,
model_id="eleven_turbo_v2_5",
language_code="nl",
voice_settings=VoiceSettings(
stability=0.0,
similarity_boost=1.0,
style=0.0,
use_speaker_boost=True,
),
)
# Play the audio back
play(response)
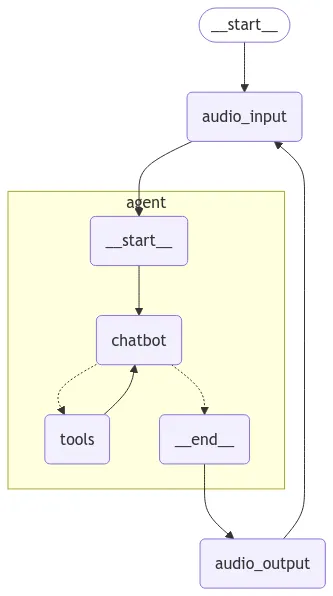
图构建:集成音频处理
在定义了处理文本和语音交互的功能后,下一步是将这些能力无缝集成到一个统一的工作流中。通过构建一个智能对话图,我们可以确保语音识别、基于文本的对话和语音响应之间的流畅衔接。
在这一阶段,我们将定义一个基于LangGraph的新工作流程,将音频输入和输出功能与聊天机器人连接起来,实现以下操作序列:
捕获音频输入:
- 聊天机器人监听用户输入,并将其从语音转换为文本。
- 一旦检测到并处理了语音,将得到的文本传递给聊天机器人进行分析。
处理基于文本的对话:
- 聊天机器人根据转录的输入和其内部逻辑生成响应。
- 它可以利用诸如日期和时间检索功能等工具来丰富交互。
生成和播放音频输出:
- 使用ElevenLabs API将聊天机器人的文本响应转换为语音。
- 将响应播放给用户,完成交互循环,并允许用户再次响应,从而无缝继续对话。
通过以这种方式构建对话工作流程,我们创建了一个动态的语音助手,能够高效地处理语音和文本交互。
以下是我们如何构建完整图以集成所有组件:
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState, END, START
# Define parent graph
builder = StateGraph(MessagesState)
# Add remote graph directly as a node
builder.add_node("audio_input", record_audio_until_silence)
builder.add_node("agent", graph)
builder.add_node("audio_output", play_audio)
builder.add_edge(START, "audio_input")
builder.add_edge("audio_input", "agent")
builder.add_edge("agent", "audio_output")
builder.add_edge("audio_output", "audio_input")
audio_graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
第三步:测试语音助手
一旦聊天机器人和音频功能完全集成,就必须对系统进行测试,以确保其流畅运行。我们将通过输入一个流式命令来启动测试对话,并观察聊天机器人的响应。
from langchain_core.messages import convert_to_messages
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
for chunk in audio_graph.stream({"messages":HumanMessage(content="Follow the user's instructions:")}, stream_mode="values", config=config):
chunk["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
结论
从头开始构建这个AI语音机器人是一次既令人兴奋又富有成就感的经历。使用预构建的工具是一回事,但从零开始开发解决方案能让我们更深入地理解各个部分是如何协同工作的。从将Whisper的语音转文本功能集成进来,到使用ElevenLabs生成栩栩如生的响应,每一步都带来了宝贵的见解和进一步定制的可能性。































