模型:
Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b
 英文
英文BLIP-2, OPT-2.7b, 仅预训练模型
BLIP-2模型利用了 OPT-2.7b (一个具有27亿参数的大语言模型)。它在李等人的论文 BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models 中首次提出,并在 this repository 中首次发布。
声明:发布BLIP-2的团队没有为这个模型编写模型卡,所以这个模型卡是由Hugging Face团队编写的。
模型描述
BLIP-2由3个模型组成:类似于CLIP的图像编码器、查询变换器(Q-Former)和一个大型语言模型。
作者从预训练的检查点中初始化图像编码器和大型语言模型的权重,并在训练查询变换器时保持它们冻结。查询变换器是一个类似于BERT的变换器编码器,将一组“查询标记”映射到查询嵌入,用来连接图像编码器和大型语言模型的嵌入空间之间的差距。
模型的目标很简单,就是根据查询嵌入和前文预测下一个文本标记。
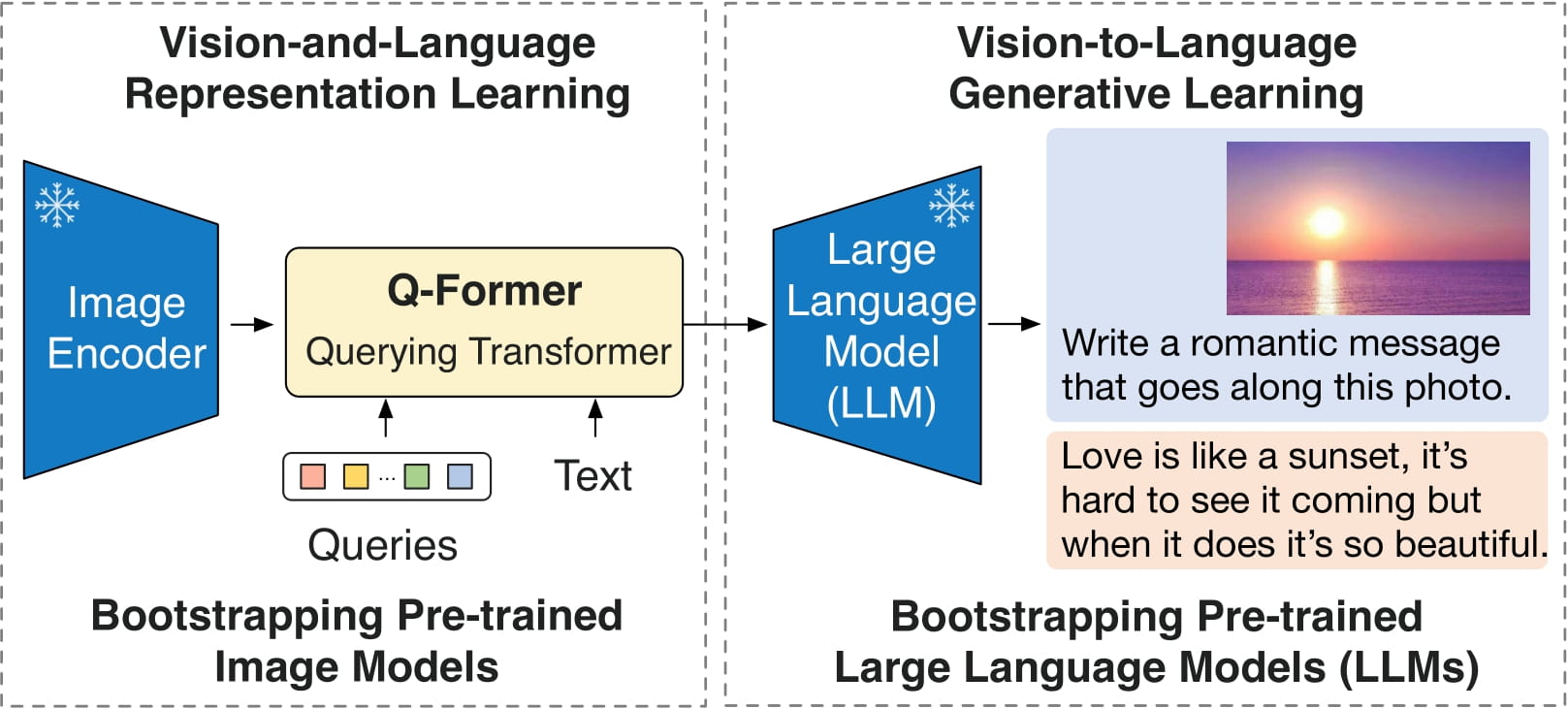
因此,该模型可以用于以下任务:
- 图像字幕
- 视觉问答(VQA)
- 通过将图像和前一个对话作为提示馈送给模型进行类似聊天的对话
直接使用和下游使用
您可以使用原始模型根据图像和可选文本生成条件文本。请参阅 model hub 以寻找您感兴趣的任务的微调版本。
偏见、风险、局限性和伦理考虑
BLIP2-OPT使用现成的OPT作为语言模型。它继承了Meta模型卡中提到的相同风险和局限性。
像其他大型语言模型一样,训练数据的多样性(或其缺乏)会对我们模型的质量产生下游影响,OPT-175B在偏见和安全性方面存在局限性。OPT-175B在生成多样性和虚构方面也可能存在质量问题。总之,OPT-175B并不能免于困扰现代大型语言模型的众多问题。
BLIP2在从互联网收集的图像文本数据集(例如 LAION )上进行了微调。因此,模型本身可能容易生成同样不合适的内容或复制底层数据中的潜在偏见。
BLIP2未在真实世界的应用中进行测试。不应直接部署该模型在任何应用中。研究人员应先仔细评估模型在特定上下文中的安全性和公平性。
使用方法
有关代码示例,请参考 documentation 。
在CPU上运行模型点击展开import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "how many dogs are in the picture?"
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt")
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
在GPU上运行模型以全精度点击展开# pip install accelerate
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "how many dogs are in the picture?"
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
以半精度(float16)运行模型点击展开# pip install accelerate
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "how many dogs are in the picture?"
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
以8位精度(int8)运行模型点击展开# pip install accelerate bitsandbytes
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
processor = Blip2Processor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
model = Blip2ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", load_in_8bit=True, device_map="auto")
img_url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/sfr-vision-language-research/BLIP/demo.jpg'
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(img_url, stream=True).raw).convert('RGB')
question = "how many dogs are in the picture?"
inputs = processor(raw_image, question, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda", torch.float16)
out = model.generate(**inputs)
print(processor.decode(out[0], skip_special_tokens=True))





















