模型:
allenai/led-large-16384-arxiv
 中文
中文Introduction
Allenai's Longformer Encoder-Decoder (LED) .
This is the official led-large-16384 checkpoint that is fine-tuned on the arXiv dataset. led-large-16384-arxiv is the official fine-tuned version of led-large-16384 . As presented in the paper , the checkpoint achieves state-of-the-art results on arxiv
Evaluation on downstream task
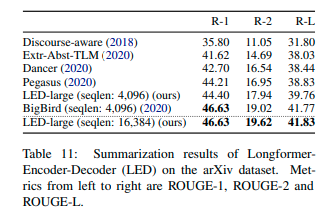
This notebook shows how led-large-16384-arxiv can be evaluated on the arxiv dataset
Usage
The model can be used as follows. The input is taken from the test data of the arxiv dataset .
LONG_ARTICLE = """"for about 20 years the problem of properties of
short - term changes of solar activity has been
considered extensively . many investigators
studied the short - term periodicities of the
various indices of solar activity . several
periodicities were detected , but the
periodicities about 155 days and from the interval
of @xmath3 $ ] days ( @xmath4 $ ] years ) are
mentioned most often . first of them was
discovered by @xcite in the occurence rate of
gamma - ray flares detected by the gamma - ray
spectrometer aboard the _ solar maximum mission (
smm ) . this periodicity was confirmed for other
solar flares data and for the same time period
@xcite . it was also found in proton flares during
solar cycles 19 and 20 @xcite , but it was not
found in the solar flares data during solar cycles
22 @xcite . _ several autors confirmed above
results for the daily sunspot area data . @xcite
studied the sunspot data from 18741984 . she found
the 155-day periodicity in data records from 31
years . this periodicity is always characteristic
for one of the solar hemispheres ( the southern
hemisphere for cycles 1215 and the northern
hemisphere for cycles 1621 ) . moreover , it is
only present during epochs of maximum activity (
in episodes of 13 years ) .
similarinvestigationswerecarriedoutby + @xcite .
they applied the same power spectrum method as
lean , but the daily sunspot area data ( cycles
1221 ) were divided into 10 shorter time series .
the periodicities were searched for the frequency
interval 57115 nhz ( 100200 days ) and for each of
10 time series . the authors showed that the
periodicity between 150160 days is statistically
significant during all cycles from 16 to 21 . the
considered peaks were remained unaltered after
removing the 11-year cycle and applying the power
spectrum analysis . @xcite used the wavelet
technique for the daily sunspot areas between 1874
and 1993 . they determined the epochs of
appearance of this periodicity and concluded that
it presents around the maximum activity period in
cycles 16 to 21 . moreover , the power of this
periodicity started growing at cycle 19 ,
decreased in cycles 20 and 21 and disappered after
cycle 21 . similaranalyseswerepresentedby + @xcite
, but for sunspot number , solar wind plasma ,
interplanetary magnetic field and geomagnetic
activity index @xmath5 . during 1964 - 2000 the
sunspot number wavelet power of periods less than
one year shows a cyclic evolution with the phase
of the solar cycle.the 154-day period is prominent
and its strenth is stronger around the 1982 - 1984
interval in almost all solar wind parameters . the
existence of the 156-day periodicity in sunspot
data were confirmed by @xcite . they considered
the possible relation between the 475-day (
1.3-year ) and 156-day periodicities . the 475-day
( 1.3-year ) periodicity was also detected in
variations of the interplanetary magnetic field ,
geomagnetic activity helioseismic data and in the
solar wind speed @xcite . @xcite concluded that
the region of larger wavelet power shifts from
475-day ( 1.3-year ) period to 620-day ( 1.7-year
) period and then back to 475-day ( 1.3-year ) .
the periodicities from the interval @xmath6 $ ]
days ( @xmath4 $ ] years ) have been considered
from 1968 . @xcite mentioned a 16.3-month (
490-day ) periodicity in the sunspot numbers and
in the geomagnetic data . @xcite analysed the
occurrence rate of major flares during solar
cycles 19 . they found a 18-month ( 540-day )
periodicity in flare rate of the norhern
hemisphere . @xcite confirmed this result for the
@xmath7 flare data for solar cycles 20 and 21 and
found a peak in the power spectra near 510540 days
. @xcite found a 17-month ( 510-day ) periodicity
of sunspot groups and their areas from 1969 to
1986 . these authors concluded that the length of
this period is variable and the reason of this
periodicity is still not understood . @xcite and +
@xcite obtained statistically significant peaks of
power at around 158 days for daily sunspot data
from 1923 - 1933 ( cycle 16 ) . in this paper the
problem of the existence of this periodicity for
sunspot data from cycle 16 is considered . the
daily sunspot areas , the mean sunspot areas per
carrington rotation , the monthly sunspot numbers
and their fluctuations , which are obtained after
removing the 11-year cycle are analysed . in
section 2 the properties of the power spectrum
methods are described . in section 3 a new
approach to the problem of aliases in the power
spectrum analysis is presented . in section 4
numerical results of the new method of the
diagnosis of an echo - effect for sunspot area
data are discussed . in section 5 the problem of
the existence of the periodicity of about 155 days
during the maximum activity period for sunspot
data from the whole solar disk and from each solar
hemisphere separately is considered . to find
periodicities in a given time series the power
spectrum analysis is applied . in this paper two
methods are used : the fast fourier transformation
algorithm with the hamming window function ( fft )
and the blackman - tukey ( bt ) power spectrum
method @xcite . the bt method is used for the
diagnosis of the reasons of the existence of peaks
, which are obtained by the fft method . the bt
method consists in the smoothing of a cosine
transform of an autocorrelation function using a
3-point weighting average . such an estimator is
consistent and unbiased . moreover , the peaks are
uncorrelated and their sum is a variance of a
considered time series . the main disadvantage of
this method is a weak resolution of the
periodogram points , particularly for low
frequences . for example , if the autocorrelation
function is evaluated for @xmath8 , then the
distribution points in the time domain are :
@xmath9 thus , it is obvious that this method
should not be used for detecting low frequency
periodicities with a fairly good resolution .
however , because of an application of the
autocorrelation function , the bt method can be
used to verify a reality of peaks which are
computed using a method giving the better
resolution ( for example the fft method ) . it is
valuable to remember that the power spectrum
methods should be applied very carefully . the
difficulties in the interpretation of significant
peaks could be caused by at least four effects : a
sampling of a continuos function , an echo -
effect , a contribution of long - term
periodicities and a random noise . first effect
exists because periodicities , which are shorter
than the sampling interval , may mix with longer
periodicities . in result , this effect can be
reduced by an decrease of the sampling interval
between observations . the echo - effect occurs
when there is a latent harmonic of frequency
@xmath10 in the time series , giving a spectral
peak at @xmath10 , and also periodic terms of
frequency @xmath11 etc . this may be detected by
the autocorrelation function for time series with
a large variance . time series often contain long
- term periodicities , that influence short - term
peaks . they could rise periodogram s peaks at
lower frequencies . however , it is also easy to
notice the influence of the long - term
periodicities on short - term peaks in the graphs
of the autocorrelation functions . this effect is
observed for the time series of solar activity
indexes which are limited by the 11-year cycle .
to find statistically significant periodicities it
is reasonable to use the autocorrelation function
and the power spectrum method with a high
resolution . in the case of a stationary time
series they give similar results . moreover , for
a stationary time series with the mean zero the
fourier transform is equivalent to the cosine
transform of an autocorrelation function @xcite .
thus , after a comparison of a periodogram with an
appropriate autocorrelation function one can
detect peaks which are in the graph of the first
function and do not exist in the graph of the
second function . the reasons of their existence
could be explained by the long - term
periodicities and the echo - effect . below method
enables one to detect these effects . ( solid line
) and the 95% confidence level basing on thered
noise ( dotted line ) . the periodogram values are
presented on the left axis . the lower curve
illustrates the autocorrelation function of the
same time series ( solid line ) . the dotted lines
represent two standard errors of the
autocorrelation function . the dashed horizontal
line shows the zero level . the autocorrelation
values are shown in the right axis . ] because
the statistical tests indicate that the time
series is a white noise the confidence level is
not marked . ] . ] the method of the diagnosis
of an echo - effect in the power spectrum ( de )
consists in an analysis of a periodogram of a
given time series computed using the bt method .
the bt method bases on the cosine transform of the
autocorrelation function which creates peaks which
are in the periodogram , but not in the
autocorrelation function . the de method is used
for peaks which are computed by the fft method (
with high resolution ) and are statistically
significant . the time series of sunspot activity
indexes with the spacing interval one rotation or
one month contain a markov - type persistence ,
which means a tendency for the successive values
of the time series to remember their antecendent
values . thus , i use a confidence level basing on
the red noise of markov @xcite for the choice of
the significant peaks of the periodogram computed
by the fft method . when a time series does not
contain the markov - type persistence i apply the
fisher test and the kolmogorov - smirnov test at
the significance level @xmath12 @xcite to verify a
statistically significance of periodograms peaks .
the fisher test checks the null hypothesis that
the time series is white noise agains the
alternative hypothesis that the time series
contains an added deterministic periodic component
of unspecified frequency . because the fisher test
tends to be severe in rejecting peaks as
insignificant the kolmogorov - smirnov test is
also used . the de method analyses raw estimators
of the power spectrum . they are given as follows
@xmath13 for @xmath14 + where @xmath15 for
@xmath16 + @xmath17 is the length of the time
series @xmath18 and @xmath19 is the mean value .
the first term of the estimator @xmath20 is
constant . the second term takes two values (
depending on odd or even @xmath21 ) which are not
significant because @xmath22 for large m. thus ,
the third term of ( 1 ) should be analysed .
looking for intervals of @xmath23 for which
@xmath24 has the same sign and different signs one
can find such parts of the function @xmath25 which
create the value @xmath20 . let the set of values
of the independent variable of the autocorrelation
function be called @xmath26 and it can be divided
into the sums of disjoint sets : @xmath27 where +
@xmath28 + @xmath29 @xmath30 @xmath31 + @xmath32 +
@xmath33 @xmath34 @xmath35 @xmath36 @xmath37
@xmath38 @xmath39 @xmath40 well , the set
@xmath41 contains all integer values of @xmath23
from the interval of @xmath42 for which the
autocorrelation function and the cosinus function
with the period @xmath43 $ ] are positive . the
index @xmath44 indicates successive parts of the
cosinus function for which the cosinuses of
successive values of @xmath23 have the same sign .
however , sometimes the set @xmath41 can be empty
. for example , for @xmath45 and @xmath46 the set
@xmath47 should contain all @xmath48 $ ] for which
@xmath49 and @xmath50 , but for such values of
@xmath23 the values of @xmath51 are negative .
thus , the set @xmath47 is empty . . the
periodogram values are presented on the left axis
. the lower curve illustrates the autocorrelation
function of the same time series . the
autocorrelation values are shown in the right axis
. ] let us take into consideration all sets
\{@xmath52 } , \{@xmath53 } and \{@xmath41 } which
are not empty . because numberings and power of
these sets depend on the form of the
autocorrelation function of the given time series
, it is impossible to establish them arbitrary .
thus , the sets of appropriate indexes of the sets
\{@xmath52 } , \{@xmath53 } and \{@xmath41 } are
called @xmath54 , @xmath55 and @xmath56
respectively . for example the set @xmath56
contains all @xmath44 from the set @xmath57 for
which the sets @xmath41 are not empty . to
separate quantitatively in the estimator @xmath20
the positive contributions which are originated by
the cases described by the formula ( 5 ) from the
cases which are described by the formula ( 3 ) the
following indexes are introduced : @xmath58
@xmath59 @xmath60 @xmath61 where @xmath62 @xmath63
@xmath64 taking for the empty sets \{@xmath53 }
and \{@xmath41 } the indices @xmath65 and @xmath66
equal zero . the index @xmath65 describes a
percentage of the contribution of the case when
@xmath25 and @xmath51 are positive to the positive
part of the third term of the sum ( 1 ) . the
index @xmath66 describes a similar contribution ,
but for the case when the both @xmath25 and
@xmath51 are simultaneously negative . thanks to
these one can decide which the positive or the
negative values of the autocorrelation function
have a larger contribution to the positive values
of the estimator @xmath20 . when the difference
@xmath67 is positive , the statement the
@xmath21-th peak really exists can not be rejected
. thus , the following formula should be satisfied
: @xmath68 because the @xmath21-th peak could
exist as a result of the echo - effect , it is
necessary to verify the second condition :
@xmath69\in c_m.\ ] ] . the periodogram values
are presented on the left axis . the lower curve
illustrates the autocorrelation function of the
same time series ( solid line ) . the dotted lines
represent two standard errors of the
autocorrelation function . the dashed horizontal
line shows the zero level . the autocorrelation
values are shown in the right axis . ] to
verify the implication ( 8) firstly it is
necessary to evaluate the sets @xmath41 for
@xmath70 of the values of @xmath23 for which the
autocorrelation function and the cosine function
with the period @xmath71 $ ] are positive and the
sets @xmath72 of values of @xmath23 for which the
autocorrelation function and the cosine function
with the period @xmath43 $ ] are negative .
secondly , a percentage of the contribution of the
sum of products of positive values of @xmath25 and
@xmath51 to the sum of positive products of the
values of @xmath25 and @xmath51 should be
evaluated . as a result the indexes @xmath65 for
each set @xmath41 where @xmath44 is the index from
the set @xmath56 are obtained . thirdly , from all
sets @xmath41 such that @xmath70 the set @xmath73
for which the index @xmath65 is the greatest
should be chosen . the implication ( 8) is true
when the set @xmath73 includes the considered
period @xmath43 $ ] . this means that the greatest
contribution of positive values of the
autocorrelation function and positive cosines with
the period @xmath43 $ ] to the periodogram value
@xmath20 is caused by the sum of positive products
of @xmath74 for each @xmath75-\frac{m}{2k},[\frac{
2m}{k}]+\frac{m}{2k})$ ] . when the implication
( 8) is false , the peak @xmath20 is mainly
created by the sum of positive products of
@xmath74 for each @xmath76-\frac{m}{2k},\big [
\frac{2m}{n}\big ] + \frac{m}{2k } \big ) $ ] ,
where @xmath77 is a multiple or a divisor of
@xmath21 . it is necessary to add , that the de
method should be applied to the periodograms peaks
, which probably exist because of the echo -
effect . it enables one to find such parts of the
autocorrelation function , which have the
significant contribution to the considered peak .
the fact , that the conditions ( 7 ) and ( 8) are
satisfied , can unambiguously decide about the
existence of the considered periodicity in the
given time series , but if at least one of them is
not satisfied , one can doubt about the existence
of the considered periodicity . thus , in such
cases the sentence the peak can not be treated as
true should be used . using the de method it is
necessary to remember about the power of the set
@xmath78 . if @xmath79 is too large , errors of an
autocorrelation function estimation appear . they
are caused by the finite length of the given time
series and as a result additional peaks of the
periodogram occur . if @xmath79 is too small ,
there are less peaks because of a low resolution
of the periodogram . in applications @xmath80 is
used . in order to evaluate the value @xmath79 the
fft method is used . the periodograms computed by
the bt and the fft method are compared . the
conformity of them enables one to obtain the value
@xmath79 . . the fft periodogram values are
presented on the left axis . the lower curve
illustrates the bt periodogram of the same time
series ( solid line and large black circles ) .
the bt periodogram values are shown in the right
axis . ] in this paper the sunspot activity data (
august 1923 - october 1933 ) provided by the
greenwich photoheliographic results ( gpr ) are
analysed . firstly , i consider the monthly
sunspot number data . to eliminate the 11-year
trend from these data , the consecutively smoothed
monthly sunspot number @xmath81 is subtracted from
the monthly sunspot number @xmath82 where the
consecutive mean @xmath83 is given by @xmath84 the
values @xmath83 for @xmath85 and @xmath86 are
calculated using additional data from last six
months of cycle 15 and first six months of cycle
17 . because of the north - south asymmetry of
various solar indices @xcite , the sunspot
activity is considered for each solar hemisphere
separately . analogously to the monthly sunspot
numbers , the time series of sunspot areas in the
northern and southern hemispheres with the spacing
interval @xmath87 rotation are denoted . in order
to find periodicities , the following time series
are used : + @xmath88 + @xmath89 + @xmath90
+ in the lower part of figure [ f1 ] the
autocorrelation function of the time series for
the northern hemisphere @xmath88 is shown . it is
easy to notice that the prominent peak falls at 17
rotations interval ( 459 days ) and @xmath25 for
@xmath91 $ ] rotations ( [ 81 , 162 ] days ) are
significantly negative . the periodogram of the
time series @xmath88 ( see the upper curve in
figures [ f1 ] ) does not show the significant
peaks at @xmath92 rotations ( 135 , 162 days ) ,
but there is the significant peak at @xmath93 (
243 days ) . the peaks at @xmath94 are close to
the peaks of the autocorrelation function . thus ,
the result obtained for the periodicity at about
@xmath0 days are contradict to the results
obtained for the time series of daily sunspot
areas @xcite . for the southern hemisphere (
the lower curve in figure [ f2 ] ) @xmath25 for
@xmath95 $ ] rotations ( [ 54 , 189 ] days ) is
not positive except @xmath96 ( 135 days ) for
which @xmath97 is not statistically significant .
the upper curve in figures [ f2 ] presents the
periodogram of the time series @xmath89 . this
time series does not contain a markov - type
persistence . moreover , the kolmogorov - smirnov
test and the fisher test do not reject a null
hypothesis that the time series is a white noise
only . this means that the time series do not
contain an added deterministic periodic component
of unspecified frequency . the autocorrelation
function of the time series @xmath90 ( the lower
curve in figure [ f3 ] ) has only one
statistically significant peak for @xmath98 months
( 480 days ) and negative values for @xmath99 $ ]
months ( [ 90 , 390 ] days ) . however , the
periodogram of this time series ( the upper curve
in figure [ f3 ] ) has two significant peaks the
first at 15.2 and the second at 5.3 months ( 456 ,
159 days ) . thus , the periodogram contains the
significant peak , although the autocorrelation
function has the negative value at @xmath100
months . to explain these problems two
following time series of daily sunspot areas are
considered : + @xmath101 + @xmath102 + where
@xmath103 the values @xmath104 for @xmath105
and @xmath106 are calculated using additional
daily data from the solar cycles 15 and 17 .
and the cosine function for @xmath45 ( the period
at about 154 days ) . the horizontal line ( dotted
line ) shows the zero level . the vertical dotted
lines evaluate the intervals where the sets
@xmath107 ( for @xmath108 ) are searched . the
percentage values show the index @xmath65 for each
@xmath41 for the time series @xmath102 ( in
parentheses for the time series @xmath101 ) . in
the right bottom corner the values of @xmath65 for
the time series @xmath102 , for @xmath109 are
written . ] ( the 500-day period ) ] the
comparison of the functions @xmath25 of the time
series @xmath101 ( the lower curve in figure [ f4
] ) and @xmath102 ( the lower curve in figure [ f5
] ) suggests that the positive values of the
function @xmath110 of the time series @xmath101 in
the interval of @xmath111 $ ] days could be caused
by the 11-year cycle . this effect is not visible
in the case of periodograms of the both time
series computed using the fft method ( see the
upper curves in figures [ f4 ] and [ f5 ] ) or the
bt method ( see the lower curve in figure [ f6 ] )
. moreover , the periodogram of the time series
@xmath102 has the significant values at @xmath112
days , but the autocorrelation function is
negative at these points . @xcite showed that the
lomb - scargle periodograms for the both time
series ( see @xcite , figures 7 a - c ) have a
peak at 158.8 days which stands over the fap level
by a significant amount . using the de method the
above discrepancies are obvious . to establish the
@xmath79 value the periodograms computed by the
fft and the bt methods are shown in figure [ f6 ]
( the upper and the lower curve respectively ) .
for @xmath46 and for periods less than 166 days
there is a good comformity of the both
periodograms ( but for periods greater than 166
days the points of the bt periodogram are not
linked because the bt periodogram has much worse
resolution than the fft periodogram ( no one know
how to do it ) ) . for @xmath46 and @xmath113 the
value of @xmath21 is 13 ( @xmath71=153 $ ] ) . the
inequality ( 7 ) is satisfied because @xmath114 .
this means that the value of @xmath115 is mainly
created by positive values of the autocorrelation
function . the implication ( 8) needs an
evaluation of the greatest value of the index
@xmath65 where @xmath70 , but the solar data
contain the most prominent period for @xmath116
days because of the solar rotation . thus ,
although @xmath117 for each @xmath118 , all sets
@xmath41 ( see ( 5 ) and ( 6 ) ) without the set
@xmath119 ( see ( 4 ) ) , which contains @xmath120
$ ] , are considered . this situation is presented
in figure [ f7 ] . in this figure two curves
@xmath121 and @xmath122 are plotted . the vertical
dotted lines evaluate the intervals where the sets
@xmath107 ( for @xmath123 ) are searched . for
such @xmath41 two numbers are written : in
parentheses the value of @xmath65 for the time
series @xmath101 and above it the value of
@xmath65 for the time series @xmath102 . to make
this figure clear the curves are plotted for the
set @xmath124 only . ( in the right bottom corner
information about the values of @xmath65 for the
time series @xmath102 , for @xmath109 are written
. ) the implication ( 8) is not true , because
@xmath125 for @xmath126 . therefore ,
@xmath43=153\notin c_6=[423,500]$ ] . moreover ,
the autocorrelation function for @xmath127 $ ] is
negative and the set @xmath128 is empty . thus ,
@xmath129 . on the basis of these information one
can state , that the periodogram peak at @xmath130
days of the time series @xmath102 exists because
of positive @xmath25 , but for @xmath23 from the
intervals which do not contain this period .
looking at the values of @xmath65 of the time
series @xmath101 , one can notice that they
decrease when @xmath23 increases until @xmath131 .
this indicates , that when @xmath23 increases ,
the contribution of the 11-year cycle to the peaks
of the periodogram decreases . an increase of the
value of @xmath65 is for @xmath132 for the both
time series , although the contribution of the
11-year cycle for the time series @xmath101 is
insignificant . thus , this part of the
autocorrelation function ( @xmath133 for the time
series @xmath102 ) influences the @xmath21-th peak
of the periodogram . this suggests that the
periodicity at about 155 days is a harmonic of the
periodicity from the interval of @xmath1 $ ] days
. ( solid line ) and consecutively smoothed
sunspot areas of the one rotation time interval
@xmath134 ( dotted line ) . both indexes are
presented on the left axis . the lower curve
illustrates fluctuations of the sunspot areas
@xmath135 . the dotted and dashed horizontal lines
represent levels zero and @xmath136 respectively .
the fluctuations are shown on the right axis . ]
the described reasoning can be carried out for
other values of the periodogram . for example ,
the condition ( 8) is not satisfied for @xmath137
( 250 , 222 , 200 days ) . moreover , the
autocorrelation function at these points is
negative . these suggest that there are not a true
periodicity in the interval of [ 200 , 250 ] days
. it is difficult to decide about the existence of
the periodicities for @xmath138 ( 333 days ) and
@xmath139 ( 286 days ) on the basis of above
analysis . the implication ( 8) is not satisfied
for @xmath139 and the condition ( 7 ) is not
satisfied for @xmath138 , although the function
@xmath25 of the time series @xmath102 is
significantly positive for @xmath140 . the
conditions ( 7 ) and ( 8) are satisfied for
@xmath141 ( figure [ f8 ] ) and @xmath142 .
therefore , it is possible to exist the
periodicity from the interval of @xmath1 $ ] days
. similar results were also obtained by @xcite for
daily sunspot numbers and daily sunspot areas .
she considered the means of three periodograms of
these indexes for data from @xmath143 years and
found statistically significant peaks from the
interval of @xmath1 $ ] ( see @xcite , figure 2 )
. @xcite studied sunspot areas from 1876 - 1999
and sunspot numbers from 1749 - 2001 with the help
of the wavelet transform . they pointed out that
the 154 - 158-day period could be the third
harmonic of the 1.3-year ( 475-day ) period .
moreover , the both periods fluctuate considerably
with time , being stronger during stronger sunspot
cycles . therefore , the wavelet analysis suggests
a common origin of the both periodicities . this
conclusion confirms the de method result which
indicates that the periodogram peak at @xmath144
days is an alias of the periodicity from the
interval of @xmath1 $ ] in order to verify the
existence of the periodicity at about 155 days i
consider the following time series : + @xmath145
+ @xmath146 + @xmath147 + the value @xmath134
is calculated analogously to @xmath83 ( see sect .
the values @xmath148 and @xmath149 are evaluated
from the formula ( 9 ) . in the upper part of
figure [ f9 ] the time series of sunspot areas
@xmath150 of the one rotation time interval from
the whole solar disk and the time series of
consecutively smoothed sunspot areas @xmath151 are
showed . in the lower part of figure [ f9 ] the
time series of sunspot area fluctuations @xmath145
is presented . on the basis of these data the
maximum activity period of cycle 16 is evaluated .
it is an interval between two strongest
fluctuations e.a . @xmath152 $ ] rotations . the
length of the time interval @xmath153 is 54
rotations . if the about @xmath0-day ( 6 solar
rotations ) periodicity existed in this time
interval and it was characteristic for strong
fluctuations from this time interval , 10 local
maxima in the set of @xmath154 would be seen .
then it should be necessary to find such a value
of p for which @xmath155 for @xmath156 and the
number of the local maxima of these values is 10 .
as it can be seen in the lower part of figure [ f9
] this is for the case of @xmath157 ( in this
figure the dashed horizontal line is the level of
@xmath158 ) . figure [ f10 ] presents nine time
distances among the successive fluctuation local
maxima and the horizontal line represents the
6-rotation periodicity . it is immediately
apparent that the dispersion of these points is 10
and it is difficult to find even few points which
oscillate around the value of 6 . such an analysis
was carried out for smaller and larger @xmath136
and the results were similar . therefore , the
fact , that the about @xmath0-day periodicity
exists in the time series of sunspot area
fluctuations during the maximum activity period is
questionable . . the horizontal line represents
the 6-rotation ( 162-day ) period . ] ] ]
to verify again the existence of the about
@xmath0-day periodicity during the maximum
activity period in each solar hemisphere
separately , the time series @xmath88 and @xmath89
were also cut down to the maximum activity period
( january 1925december 1930 ) . the comparison of
the autocorrelation functions of these time series
with the appriopriate autocorrelation functions of
the time series @xmath88 and @xmath89 , which are
computed for the whole 11-year cycle ( the lower
curves of figures [ f1 ] and [ f2 ] ) , indicates
that there are not significant differences between
them especially for @xmath23=5 and 6 rotations (
135 and 162 days ) ) . this conclusion is
confirmed by the analysis of the time series
@xmath146 for the maximum activity period . the
autocorrelation function ( the lower curve of
figure [ f11 ] ) is negative for the interval of [
57 , 173 ] days , but the resolution of the
periodogram is too low to find the significant
peak at @xmath159 days . the autocorrelation
function gives the same result as for daily
sunspot area fluctuations from the whole solar
disk ( @xmath160 ) ( see also the lower curve of
figures [ f5 ] ) . in the case of the time series
@xmath89 @xmath161 is zero for the fluctuations
from the whole solar cycle and it is almost zero (
@xmath162 ) for the fluctuations from the maximum
activity period . the value @xmath163 is negative
. similarly to the case of the northern hemisphere
the autocorrelation function and the periodogram
of southern hemisphere daily sunspot area
fluctuations from the maximum activity period
@xmath147 are computed ( see figure [ f12 ] ) .
the autocorrelation function has the statistically
significant positive peak in the interval of [ 155
, 165 ] days , but the periodogram has too low
resolution to decide about the possible
periodicities . the correlative analysis indicates
that there are positive fluctuations with time
distances about @xmath0 days in the maximum
activity period . the results of the analyses of
the time series of sunspot area fluctuations from
the maximum activity period are contradict with
the conclusions of @xcite . she uses the power
spectrum analysis only . the periodogram of daily
sunspot fluctuations contains peaks , which could
be harmonics or subharmonics of the true
periodicities . they could be treated as real
periodicities . this effect is not visible for
sunspot data of the one rotation time interval ,
but averaging could lose true periodicities . this
is observed for data from the southern hemisphere
. there is the about @xmath0-day peak in the
autocorrelation function of daily fluctuations ,
but the correlation for data of the one rotation
interval is almost zero or negative at the points
@xmath164 and 6 rotations . thus , it is
reasonable to research both time series together
using the correlative and the power spectrum
analyses . the following results are obtained :
1 . a new method of the detection of statistically
significant peaks of the periodograms enables one
to identify aliases in the periodogram . 2 . two
effects cause the existence of the peak of the
periodogram of the time series of sunspot area
fluctuations at about @xmath0 days : the first is
caused by the 27-day periodicity , which probably
creates the 162-day periodicity ( it is a
subharmonic frequency of the 27-day periodicity )
and the second is caused by statistically
significant positive values of the autocorrelation
function from the intervals of @xmath165 $ ] and
@xmath166 $ ] days . the existence of the
periodicity of about @xmath0 days of the time
series of sunspot area fluctuations and sunspot
area fluctuations from the northern hemisphere
during the maximum activity period is questionable
. the autocorrelation analysis of the time series
of sunspot area fluctuations from the southern
hemisphere indicates that the periodicity of about
155 days exists during the maximum activity period
. i appreciate valuable comments from professor j.
jakimiec ."""
from transformers import LEDForConditionalGeneration, LEDTokenizer
import torch
tokenizer = LEDTokenizer.from_pretrained("allenai/led-large-16384-arxiv")
input_ids = tokenizer(LONG_ARTICLE, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to("cuda")
global_attention_mask = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
# set global_attention_mask on first token
global_attention_mask[:, 0] = 1
model = LEDForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("allenai/led-large-16384-arxiv", return_dict_in_generate=True).to("cuda")
sequences = model.generate(input_ids, global_attention_mask=global_attention_mask).sequences
summary = tokenizer.batch_decode(sequences)





















