推出txtai:一款拥有先进文本嵌入能力的人工智能集成数据库
搜索是许多应用程序的基础。一旦数据开始堆积,用户希望能够找到它。它是互联网的基础,也是一个永远没有解决或完成的不断增长的挑战。
自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing,NLP)领域正迅速发展,出现了许多新的技术。大规模的通用语言模型是一种令人兴奋的新能力,使我们能够添加令人惊叹的功能。创新不断进行,新的模型和进展似乎每周都在涌现。
本文介绍txtai,一款一体化嵌入数据库,可以在任何应用程序中实现基于自然语言理解(Natural Language Understanding,NLU)的搜索功能。
介绍txtai
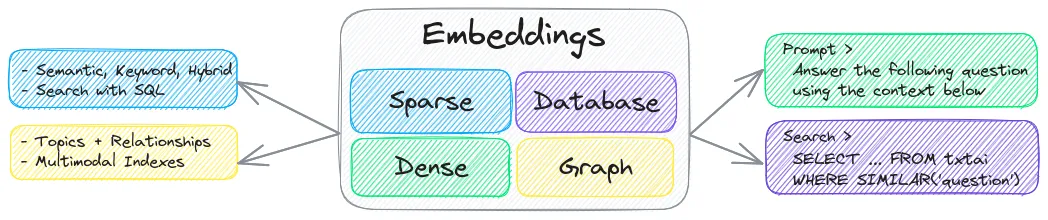
txtai是一款面向语义搜索、LLM编排和语言模型工作流程的全能嵌入式数据库。
嵌入式数据库结合了向量索引(稀疏和稠密)、图网络和关系数据库。这使得可以通过SQL进行向量搜索,进行主题建模,增强检索生成等操作。
嵌入式数据库可以独立存在,也可以作为大型语言模型(LLM)提示的强大知识源。
以下是主要功能的摘要:
1. 通过SQL、对象存储、主题建模、图分析和多模式索引进行向量搜索
2. 为文本、文档、音频、图像和视频创建嵌入
3. 基于语言模型的流水线,可运行LLM提示、问答、标注、转录、翻译、摘要等任务
4. 将流水线组合成工作流,并聚合业务逻辑。txtai的处理可以是简单的微服务或多模型工作流。
5. 使用Python或YAML构建。提供JavaScript、Java、Rust和Go的API绑定。
6. 可以在本地运行或通过容器编排进行扩展
txtai使用Python 3.8+、Hugging Face Transformers、Sentence Transformers和FastAPI构建。txtai是在Apache 2.0许可下的开源项目。
安装并运行txtai
txtai可以通过pip或Docker安装。下面展示了如何通过pip进行安装。
pip install txtai语义搜索
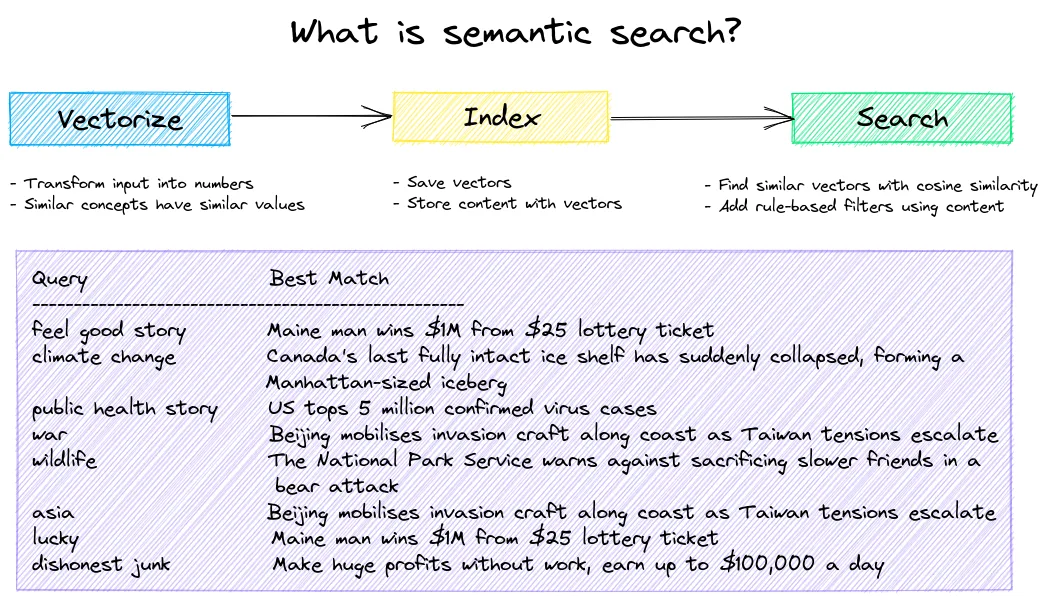
嵌入式数据库是提供语义搜索的引擎。数据被转化为嵌入向量,其中类似的概念会产生相似的向量。使用这些向量构建各种大小的索引。这些索引用于查找具有相同含义而不一定是相同关键词的结果。
嵌入式数据库的基本用例是为语义搜索构建近似最近邻(ANN)索引。下面的示例索引了一小部分文本条目,以展示语义搜索的价值。
from txtai import Embeddings
# Works with a list, dataset or generator
data = [
"US tops 5 million confirmed virus cases",
"Canada's last fully intact ice shelf has suddenly collapsed, forming a Manhattan-sized iceberg",
"Beijing mobilises invasion craft along coast as Taiwan tensions escalate",
"The National Park Service warns against sacrificing slower friends in a bear attack",
"Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket",
"Make huge profits without work, earn up to $100,000 a day"
]
# Create an embeddings
embeddings = Embeddings(path="sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2")
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index(data)
print("%-20s %s" % ("Query", "Best Match"))
print("-" * 50)
# Run an embeddings search for each query
for query in ("feel good story", "climate change",
"public health story", "war", "wildlife", "asia",
"lucky", "dishonest junk"):
# Extract uid of first result
# search result format: (uid, score)
uid = embeddings.search(query, 1)[0][0]
# Print text
print("%-20s %s" % (query, data[uid]))

上面的示例显示,对于所有的查询,查询文本都不在数据中。这就是基于transformer模型的真正优势,相比于基于标记的搜索。你会得到即开即用的功能。
更新和删除
对于嵌入式数据,txtai也提供了支持。upsert操作将插入新数据并更新现有数据。
以下部分运行一个查询,然后更新一个值来更改顶部结果,最后删除更新后的值以恢复到原始查询结果。
# Run initial query
uid = embeddings.search("feel good story", 1)[0][0]
print("Initial: ", data[uid])
# Create a copy of data to modify
udata = data.copy()
# Update data
udata[0] = "See it: baby panda born"
embeddings.upsert([(0, udata[0], None)])
uid = embeddings.search("feel good story", 1)[0][0]
print("After update: ", udata[uid])
# Remove record just added from index
embeddings.delete([0])
# Ensure value matches previous value
uid = embeddings.search("feel good story", 1)[0][0]
print("After delete: ", udata[uid])
Initial: Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket
After update: See it: baby panda born
After delete: Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket
坚持
嵌入可以保存到存储和重新加载。
embeddings.save("index")
embeddings = Embeddings()
embeddings.load("index")
uid = embeddings.search("climate change", 1)[0][0]
print(data[uid])
Canada's last fully intact ice shelf has suddenly collapsed, forming a
Manhattan-sized iceberg
混合搜索
虽然密集向量索引是迄今为止语义搜索系统的最佳选择,但稀疏关键字索引仍然可以增加价值。在某些情况下,找到完全匹配可能很重要。
混合搜索将稀疏和密集向量索引的结果结合起来,以获得两者的最佳效果。
# Create an embeddings
embeddings = Embeddings(
hybrid=True,
path="sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2"
)
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index(data)
print("%-20s %s" % ("Query", "Best Match"))
print("-" * 50)
# Run an embeddings search for each query
for query in ("feel good story", "climate change",
"public health story", "war", "wildlife", "asia",
"lucky", "dishonest junk"):
# Extract uid of first result
# search result format: (uid, score)
uid = embeddings.search(query, 1)[0][0]
# Print text
print("%-20s %s" % (query, data[uid]))

与语义搜索的结果相同。让我们运行仅使用关键字索引的相同示例来查看这些结果。
# Create an embeddings
embeddings = Embeddings(keyword=True)
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index(data)
print(embeddings.search("feel good story"))
print(embeddings.search("lottery"))
[]
[(4, 0.5234998733628726)]
当嵌入实例只使用关键字索引时,它不能找到语义匹配,只能找到关键字匹配。
内容存储
到目前为止,所有的示例都是引用原始的数据数组来检索输入文本。这对于演示来说效果很好,但如果你有数百万个文档怎么办?在这种情况下,文本需要通过id从外部数据存储中检索出来。
内容存储添加了一个关联的数据库(如SQLite、DuckDB),它将与向量索引一起存储相关的元数据。文档文本、附加元数据和其他对象可以直接与索引的向量一起存储和检索。
# Create embeddings with content enabled.
# The default behavior is to only store indexed vectors.
embeddings = Embeddings(
path="sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2",
content=True,
objects=True
)
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index(data)
print(embeddings.search("feel good story", 1)[0]["text"])
Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket上面唯一的更改是将content标志设置为True。这样就可以在索引旁边存储文本和元数据内容(如果提供的话)。请注意,文本是如何从查询结果中提取的!
SQL查询
当启用内容时,将存储整个字典并可以查询。除了矢量查询,txtai还接受SQL查询。这支持使用矢量索引和存储在数据库后端的内容进行组合查询。
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index([{"text": text, "length": len(text)} for text in data])
# Filter by score
print(embeddings.search("select text, score from txtai where similar('hiking danger') and score >= 0.15"))
# Filter by metadata field 'length'
print(embeddings.search("select text, length, score from txtai where similar('feel good story') and score >= 0.05 and length >= 40"))
# Run aggregate queries
print(embeddings.search("select count(*), min(length), max(length), sum(length) from txtai"))
[{'text': 'The National Park Service warns against sacrificing slower friends in a bear attack', 'score': 0.3151373863220215}]
[{'text': 'Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket', 'length': 42, 'score': 0.08329027891159058}]
[{'count(*)': 6, 'min(length)': 39, 'max(length)': 94, 'sum(length)': 387}]
上面的示例添加了一个简单的附加字段,文本长度。
注意,第二个查询是根据元数据字段长度以及一个类似的查询子句进行过滤的。这是矢量搜索与传统过滤的完美结合,有助于识别最佳结果。
对象存储
除了元数据之外,二进制内容还可以与文档相关联。下面的示例下载一个图像,并将其与相关文本一起插入到嵌入索引中。
import urllib
from IPython.display import Image
# Get an image
request = urllib.request.urlopen("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neuml/txtai/master/demo.gif")
# Upsert new record having both text and an object
embeddings.upsert([("txtai", {"text": "txtai executes machine-learning workflows to transform data and build AI-powered semantic search applications.", "object": request.read()}, None)])
# Query txtai for the most similar result to "machine learning" and get associated object
result = embeddings.search("select object from txtai where similar('machine learning') limit 1")[0]["object"]
# Display image
Image(result.getvalue(), width=600)
主题建模
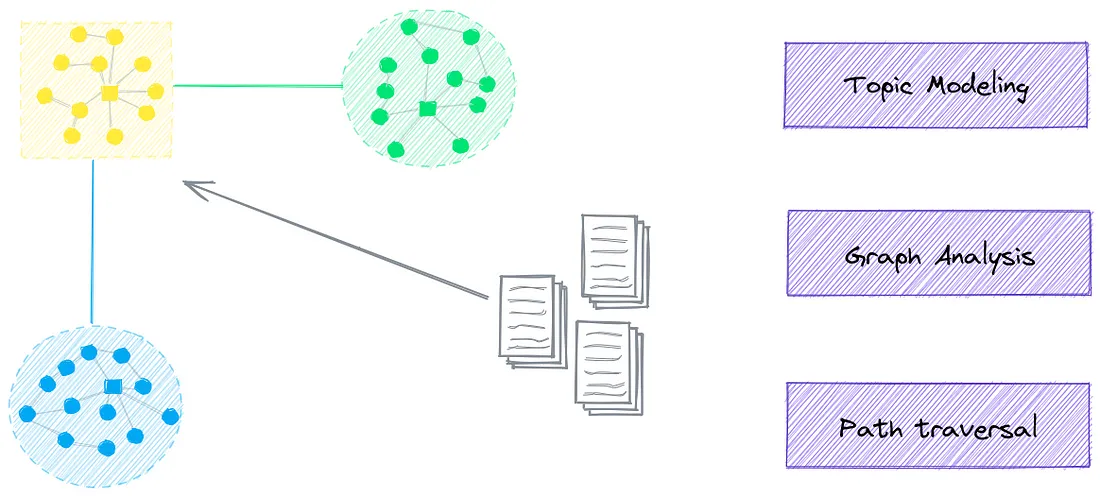
主题建模是通过语义图实现的。语义图也称为知识图或语义网络,它构建了一个节点之间具有语义关系的图网络。总之,它们可以利用嵌入索引中固有的关系。
# Create embeddings with a graph index
embeddings = Embeddings(
path="sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2",
content=True,
functions=[
{"name": "graph", "function": "graph.attribute"},
],
expressions=[
{"name": "category", "expression": "graph(indexid, 'category')"},
{"name": "topic", "expression": "graph(indexid, 'topic')"},
],
graph={
"topics": {
"categories": ["health", "climate", "finance", "world politics"]
}
}
)
embeddings.index(data)
embeddings.search("select topic, category, text from txtai")
[{'topic': 'us_cases_million_confirmed',
'category': 'finance',
'text': 'US tops 5 million confirmed virus cases'},
{'topic': "canada's_iceberg_suddenly_forming",
'category': 'climate',
'text': "Canada's last fully intact ice shelf has suddenly collapsed, forming a Manhattan-sized iceberg"},
{'topic': 'coast_taiwan_mobilises_escalate',
'category': 'world politics',
'text': 'Beijing mobilises invasion craft along coast as Taiwan tensions escalate'}]
当启用图形索引时,将为嵌入实例中的每个条目分配主题。主题是通过社区检测算法分组的图节点上的稀疏索引动态创建的。
如上所示,还派生了主题类别。
子索引
可以为嵌入配置子索引。单个嵌入实例可以有多个子索引,每个子索引具有不同的配置。
我们将构建一个包含关键字和密集索引的嵌入索引来进行演示。
# Create embeddings with subindexes
embeddings = Embeddings(
content=True,
defaults=False,
indexes={
"keyword": {
"keyword": True
},
"dense": {
"path": "sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2"
}
}
)
embeddings.index(data)
embeddings.search("feel good story", limit=1, index="keyword")[]embeddings.search("feel good story", limit=1, index="dense")[{'id': '4',
'text': 'Maine man wins $1M from $25 lottery ticket',
'score': 0.08329027891159058}]
这个例子再次说明了关键字搜索和语义搜索之间的区别。第一次搜索调用使用定义的关键字索引,第二次搜索调用使用密集向量索引。
LLM编排
txtai是一款全能的嵌入式数据库。它是唯一一个同时支持稀疏索引、图网络和关系数据库,并支持内联SQL的向量数据库。除此之外,txtai还支持LLM编排。
提取器流水线是txtai对检索增强生成(RAG)的改进。该流水线通过将提示、上下文数据存储和生成模型结合起来,从内容中提取知识。
下面的示例展示了如何使用嵌入式数据库作为上下文的大型语言模型(LLM)。
import torch
from txtai.pipeline import Extractor
def prompt(question):
return [{
"query": question,
"question": f"""
Answer the following question using the context below.
Question: {question}
Context:
"""
}]
# Create embeddings
embeddings = Embeddings(
path="sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2",
content=True,
autoid="uuid5"
)
# Create an index for the list of text
embeddings.index(data)
# Create and run extractor instance
extractor = Extractor(
embeddings,
"google/flan-t5-large",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
output="reference"
)
extractor(prompt("What country is having issues with climate change?"))[0]
{'answer': 'Canada', 'reference': 'da633124-33ff-58d6-8ecb-14f7a44c042a'}上述逻辑首先构建了一个嵌入式索引。然后加载一个LLM,并使用嵌入式索引来驱动LLM提示。
提取器流水线还可以选择性地返回与答案最佳匹配的记录的 ID 引用。该 id 可以用于解析完整的答案引用。
uid = extractor(prompt("What country is having issues with climate change?"))[0]["reference"]
embeddings.search(f"select id, text from txtai where id = '{uid}'")
[{'id': 'da633124-33ff-58d6-8ecb-14f7a44c042a',
'text': "Canada's last fully intact ice shelf has suddenly collapsed, forming a Manhattan-sized iceberg"}]
LLM推理也可以独立运行。
from txtai.pipeline import LLM
llm = LLM("google/flan-t5-large", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
llm("Where is one place you'd go in Washington, DC?")
national museum of american history语言模型工作流
语言模型工作流,也被称为语义工作流,将语言模型连接在一起,构建智能应用程序。
工作流可以直接在嵌入式实例旁运行,类似于关系数据库中的存储过程。工作流可以使用Python或YAML编写。我们将演示如何使用YAML编写工作流。
# Embeddings instance
writable: true
embeddings:
path: sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2
content: true
functions:
- {name: translation, argcount: 2, function: translation}
# Translation pipeline
translation:
# Workflow definitions
workflow:
search:
tasks:
- search
- action: translation
args:
target: fr
task: template
template: "{text}"
上面的工作流加载了一个嵌入索引并定义了一个搜索工作流。搜索工作流运行搜索,然后将结果传递给翻译管道。翻译管道将结果翻译成法语。
from txtai import Application
# Build index
app = Application("embeddings.yml")
app.add(data)
app.index()
# Run workflow
list(app.workflow(
"search",
["select text from txtai where similar('feel good story') limit 1"]
))
['Maine homme gagne $1M à partir de $25 billet de loterie']
在某些情况下,SQL函数可以完成与工作流相同的工作。下面的函数将转换管道作为函数运行。
app.search("select translation(text, 'fr') text from txtai where similar('feel good story') limit 1")[{'text': 'Maine homme gagne $1M à partir de $25 billet de loterie'}]带有模板的LLM链也可以用于工作流。工作流是自包含的,它们可以使用或不使用关联的嵌入实例来操作。下面的工作流使用LLM有条件地将文本翻译为法语,然后检测文本的语言。
sequences:
path: google/flan-t5-large
torch_dtype: torch.bfloat16
workflow:
chain:
tasks:
- task: template
template: Translate '{statement}' to {language} if it's English
action: sequences
- task: template
template: What language is the following text? {text}
action: sequences
inputs = [
{"statement": "Hello, how are you", "language": "French"},
{"statement": "Hallo, wie geht's dir", "language": "French"}
]
app = Application("workflow.yml")
list(app.workflow("chain", inputs))
['French', 'German']结论
NLP正在快速发展。一年前还不可能的事情现在都成为可能了。本文介绍了一体化嵌入式数据库txtai。































